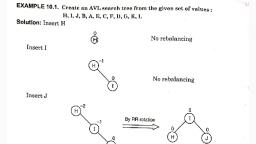
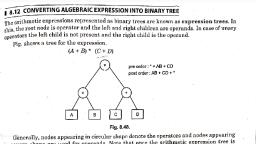
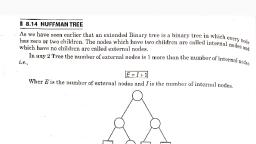
Page 1 :
Switching Techniques, , In large networks there might be multiple paths linking sender, and receiver. Information may be switched as it travels through, various communication channels. There are three typical, switching techniques available for digital traffic., , * Circuit Switching, , ¢ Message Switching, ¢ Packet Switching, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 2 :
Circuit Switching, , Circuit switching is a technique that directly connects the, sender and the receiver in an unbroken path., , Telephone switching equipment, for example, establishes a, path that connects the caller's telephone to the receiver's, telephone by making a physical connection., , In this type of switching technique, once a connection is, established, a dedicated path exists between both ends until, the connection is terminated., , Routing decisions must be made when the circuit is first, established, but decisions cannot be made after that time., , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
Circuit Switching, , Circuit switching networks operate almost the same way as, the telephone system works., , A complete end-to-end path must exist before communication, can take place., , The computer initiating the data transfer must ask for a, connection to the destination., , Before the establishment of the connection, the destination, must send the acknowledge to the source node to indicate that, it is ready and willing to send/receive data., , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
Circuit switching, , Advantages:, ¢ The communication channel (once established) is dedicated., , Disadvantages:, , ¢ Possible long wait to establish a connection, (10 seconds,, more on long- distance or international calls.) during which, no data can be transmitted., , ¢ More expensive than any other switching techniques,, because a dedicated path is required for each connection., , ¢ Inefficient use of the communication channel, because the, channel is not used when the connected systems are not, using it., , Scanned with CamScanner