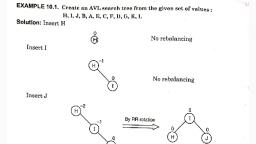
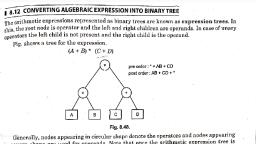
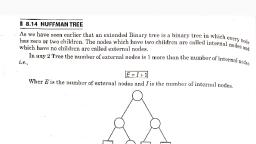
Page 1 :
1. Network Basics, 1.1 What is Network?, A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources, (such as printers and CDs), exchange files, or allow electronic communications. The, computers on a network may be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio waves,, satellites, or infrared light beams., Two very common types of networks include:, •, •, , Local Area Network (LAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), , 1.2 Peer-to-peer Network, In a peer-to-peer network, all computers are considered equal; they all have the same, abilities to use the resources available on the network. Peer-to-peer networks are designed, primarily for small to medium local area networks. Nearly all modern desktop operating, systems, such as Macintosh OSX, Linux, and Windows, can function as peer-to-peer network, operating systems., , Fig. 1. Peer-to-peer network, •, , Advantages of a peer-to-peer network:, o Less initial expense - No need for a dedicated server., o Setup - An operating system (such as Windows XP) already in place may only, need to be reconfigured for peer-to-peer operations., • Disadvantages of a peer-to-peer network:, o Decentralized - No central repository for files and applications., o Security - Does not provide the security available on a client/server, network., 1.3 Server-Client Network
Page 2 :
A client-server network is a computer network that uses a dedicated computer (server) to, store data, provide/manage resources and control user access. The server acts as a central, point on the network upon which the other computers connect to., A computer that connects to the server is called a client., , 1.2 Client Server Network Diagram, A client-server network is usually preferred over a peer-to-peer network that doesn’t have a, central server to manage the network., A client-server network may have more than one server, each dedicated to handling a specific, function. Functions may include:, o, o, o, o, o, o, o, o, o, o, o, •, , Data storage, Handling security, Hosting shared applications, Managing an internet connection, Scheduling and running backups, Email services, Print jobs, Domain name services, Storing usernames and passwords to control access, Assigning levels of access to resources, Monitoring network traffic, , Benefits of a client-server network:, o Generally more secure than peer-to-peer networks, o One client computer crashing does not effect the other computers, o Easier to recover files as backups can be controlled centrally by the network, administrator, o Files and resources are easier to share and control from server, o Improved levels of security as files are centralised, o It’s easier to administrate the whole network using a server, o Faster performance as each computer is only fulfilling one role, o Security is potentially cheaper and easier when done centrally, o Individual users do not have to worry about backups or security
Page 3 :
•, , o Larger networks can be created, Drawbacks of a client-server network:, o Servers can be expensive to buy and maintain, o A network technician will often be required, o Trickier to set up with specialist knowledge needed, o Over-all set up cost is more expensive than a peer-to-peer network, o Server failure will probably disrupt all computers on the network