Page 1 :
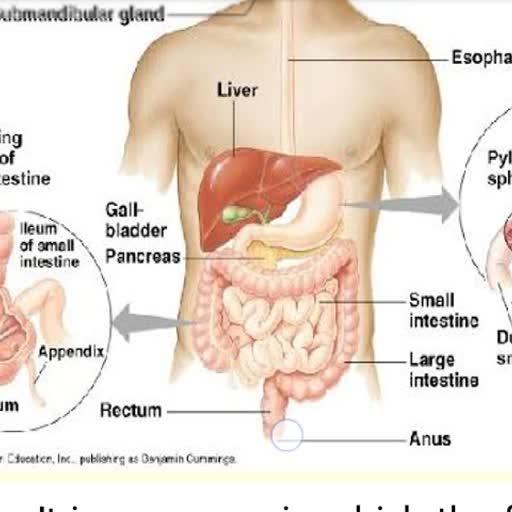
Organisms need material from outside in order to, grow, develop and synthesize proteins and other, substances needed by our body. For this, nutrition, is important in our body., , Nutrition:- It is the process of intake of food to, produce energy required for various metabolic, activities of the body., , There are two types of metabolic processes, , occurring in our body : Catabolic and Anabolic, , - Catabolic processes include, , , , synthesis processes., The food that we eat has nutrients in it which, provide energy., , , , 1. Carbohydrates, 2. Vitamins, , 3. Proteins, , 4. Fats, , 5. Minerals, , , , On the basis of how organisms obtain food, they, are of two main types: Autotrophic nutrition and, Heterotrophic nutrition., , 1. Autotrophic nutrition:- It is a type of nutrition in, which organisms can make its food with the help of, Photosynthesis as they possess Chlorophyll. That is,, they have the ability to convert solar energy into, chemical energy for food, but this power is only in, green plants and not animals or humans as they, don’t have any photosynthetic pigment., , For example - In all green plants, the, photosynthetic pigments are Chlorophyll,, Carotenoids, Phycobilins, etc. Out of all, Chlorophyll, a and Chlorophyll b are the best., , ion:- It is a type of nutrition, in which organisms cannot make their own food as, it lacks chlorophyll or any other photosynthetic, pigments., , For example —all non green plants & animals, , , , , , , , how they obtain nutrition from autotrophs,, hetrotrophes show different modes of obtaining, food: either they act as Parasites, as Saprophytes, or show Holozoic mode., , on dead decaying matter. For example- fungi., , They secrete certain enzymes from their body, surface that convert complex food into simple form, and then they absorb it through general body, surface., , 2. Parasites:- They are organisms that live in or on, the surface of other organisms to fulfill their, nutritional requirements., , For example —lices in human head., , This relationship can be symbiotic or non symbiotic., vSymbio., in which both the partners are mutually benefited, like e.coli in human intestine as it obtains its food, from our body but in response, secretes certain, minerals for our body., , For example —e.coli bacterium (parasite) in human, intestine (host), , 3. Holozoic_mode:- They are organisms that, follow five steps in sequence: ingestion, digestion,, absorption, assimilation & egestion, , For example: man, , (Organism showing this mode can be Herbivorous,, Carnivorous or Omnivorous), , , , , , , , Nutrition in Animals, Digestive System of man, Man is a heterotroph & has a holozoic mode of, nutrition. The digestive system of man is divided, into two parts:, metre long tube that starts from mouth and ends, up at anus., + Bucal cavity * Oesophagus + Stomach + Small, intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum & lleum) + Large, intestine (Caecum, Colon & Rectum), 1) Salivary gland- Saliva containing starch is called, Ptyalin (Serum Amylase)., , Anatomy of the Salivary Glands, , ymon, noses, , Tongue, ‘subingutoland—*
Page 2 :
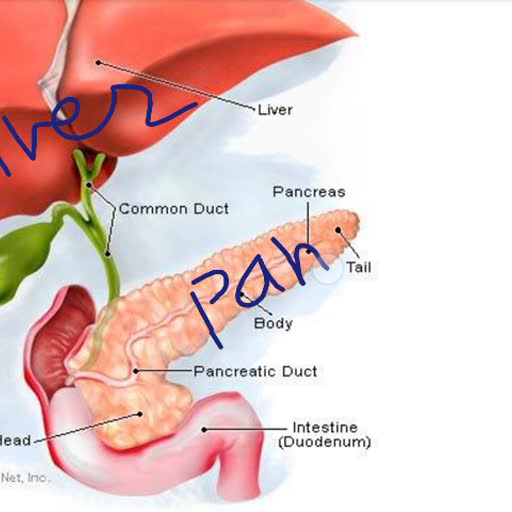
2) Gastric_gland- They produce various gastric, juices like:, , i. Mucus: It lines the stomach wall., , ii Hydrochloric Acid- It provides an acidic medium., iii.Pepsinogen- It helps convert proteins to, Peptones., , iv. Renin- It helps to change milk to curd., , , , , , 3), i. Amylase- It helps in converting starch to maltose., ii. Trypsin- It helps in converting Peptones to, Peptides., iii. Lipase- Helps in converting fats to fatty acid &, glycerol., , Galleindeer, , 4) Liver produces bile juices which help in digestion, of fats., , 5) Gland in lleum prepares erepsin which helps in, converting the following, i. Peptides to amino acid, , ii. Lipase/ fat to fatty acid & glycerin, , iii. Maltase/ maltose to glucose, , iv. Lactase/ lactose to galactose, , , , , , , , , Mouth, , Esophagus, Stomach, Liver, Gallbladder Pancreas, , (under stomach), Large intestine Small intestine, , Rectum, , The human digestive system, , , , , , {Tongue, Salivary) Parotid gland, glands” Sublingual gland, , Submandibular gland, , Oral cavity, Pharynx, , Ascending, portion off, large intestine, , , , , , , —smet \., imeating, Duodenum of, , + —Lerge small intestine, intosting, , , , Anus, , , , Ingestion: It is a process in which the food is taken, in mouth and churned with the help of teeth., , , , : In the mouth, saliva is secreted through, salivary gland that contains serum amylase which, starts the digestion of starch. The masticated food, is rolled into bolus and is swallowed. Then the food,, from food pipe, by peristaltic movement passes, into the stomach ., , In St ch: When the food goes in the stomach,, gastric juices are secreted i.e.,, , Mucus: That lines the stomach wall., , Hydrochloric Acid- That provides an acidic medium, for Pepsin., , Pepsin- That converts proteins to Peptones., , Renin- That changes milk to curd., , , , Food remains in the stomach for about 3 hours and, then is passed into the duodenum in the form of, chyme., , e In Duodenum the bile juices, bicarbonates, ions from liver & pancreatic juice from, pancreas are secreted., , e Then the bile juice helps in emulsification of, fats., , e The bicarbonates ions provide alkaline, medium to pancreatic juices., , e The pancreatic juices help in converting, amylase and starch into maltose., , e Also trypsin helps to convert peptones to, peptides., , e Lipase also helps to convert fat into fatty, acid & glycerol.
Page 3 :
e Then the food passes from jejunum to ileum., In ileum intestinal juice is secreted that, completes the digestion and converts food, into soluble form i.e. amino acid, fatty acid &, glucose.., Absorption: In ileum there are small finger like, projections called villi that increase the surface, area for absorption. Absorbed food is passed into, blood & through blood, diffuses into body cells., , Assimil, from absorbed food ., , , , Egestion:The undigested food passes through the, large intestine & water absorption take place. This, undigested food from caecum passes to colon and, then to rectum where it forms faeces and is, egested through anus., , , , Peptic Ulcer: It is a disorder when mucus, membrane of stomach gets corroded due to which, acid effect reaches stomach wall which leads to, ulcers., , Peptic ulcer, , Healthy, , Duodenal ulcer, , Stomach ulcer