Page 1 :
Life Process, Class 10, , Part - 1
Page 2 :
Criteria to decide whether something is alive, • The most important criteria to decide whether something is, alive is movement., movement, , Visible, Movements, , ✓ movements of body parts., , Invisible, Movements, , √ molecular movements., √ molecular movements in cells and, tissues is necessary for all life process.
Page 3 :
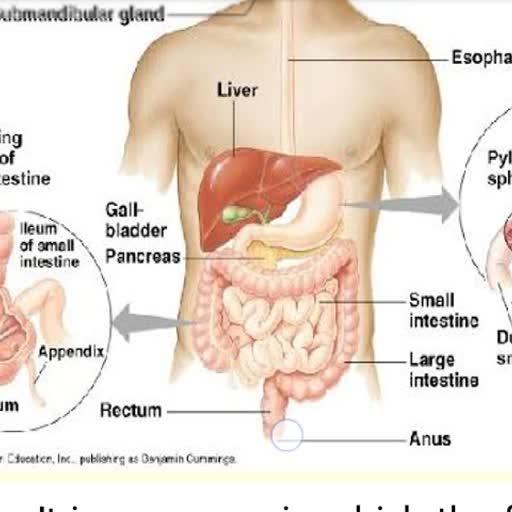
Life Processes, Life processes are the basic processes in living organisms which, are necessary for maintaining their life. The basic life processes, are - nutrition, respiration, transportation and excretion., is the process of taking food by an organism and its, Nutrition, utilisation by the body for life processes., Respiration, Transportation, Excretion, , is the process by which digest food is burnt in the cells of, the body with the help of oxygen to release energy., is the process by which food, oxygen, water and waste, products are carried from one part of body to the other., is the process by which waste products are removed from, the body.
Page 4 :
Nutrition, • Nutrition is the process of taking food by an organism and its, utilisation by the body to build the body, for growth, to repair the, damaged parts of the body and for energy., • Life on the earth depends on carbon based molecules and most of, the food also carbon based molecules. The outside raw materials, Autotrophic, used by living organisms are food, water and air., , Modes of nutrition, Autotrophic, Nutrition, , Nutrition, Heterotrophic, Nutrition, , is the nutrition in which organisms prepare their own food, from simple inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and, water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll., Eg :- all green plants and some bacteria.
Page 5 :
Heterotrophic, Nutrition, , is nutrition in which organisms get their food directly, or indirectly from plants., Eg :- all animals, fungi and some bacteria., Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition, , i) Saprophytic, Nutrition, , ii) Parasitic, Nutrition, , is nutrition in which organisms get their food from dead and, decaying organisms. They break down the food material, outside their body and then absorbs it., Eg :- mushroom, bread mould, yeast p, some bacteria etc, is nutrition in which organisms get their food from living, organisms (host) without killing them., Eg :- cuscuta, orchids, ticks, lice, leeches, round worm,, plasmodium, etc
Page 6 :
iii) Holozoic, Nutrition, , is nutrition in which organisms take food directly and then, digests and absorbs it., Eg:- amoeba, paramaecium, birds, fishes, humans, etc, Nutrition in Plants, , Photosynthesis, , is the process by which plants prepare food by using, carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and, chlorophyll. The food prepared is carbohydrate which is, stored in the form starch. Oxygen is released in this, process.
Page 7 :
Process of Photosynthesis, , Photosynthesis takes place in three main steps., 1. Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll., 2. Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and splitting up of, water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen., 3. Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrates.
Page 8 :
Chlorophyll, , are the green pigments present in the leaves. If we observe a, cross section of a leaf under a microscope, we can see cells, containing green dot like structures called chloroplast which, contains chlorophyll.
Page 9 :
Stomata, , are tiny pores present in the leaves through which exchange, of gases takes place. Each stomata has a pair of guard cells, which controls the opening and closing of the stomatal pore., When water enters the guard cells, it swells and the pore, opens qnd when the guard cells lose water, it shrinks and the, pore close.