Page 1 :
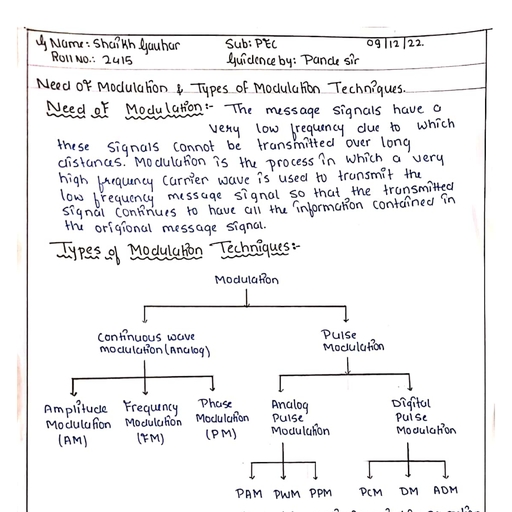
Amplitude Modulation, , Syllabus :, Need for modulation, Types of modulation techniques, Amplitude modulation : Mathematical representation of, amplitude modulated wave, Modulation index, Bandwidth requirement, Representation of AM signal in time and, frequency domain, Types of AM with respect to frequency spectrum (DSB, SSB and VSB), Power relations in AM, wave., , , , 2.1. Baseband Transmission (Transmission without Modulation) :, , — Insome systems, called the baseband transmission systems, the baseband signals (original information signals) are converted into, electrical signals and transmitted directly., , — An example of these type of systems is telephone networks where the sound signal converted into the electrical signal is placed, directly on the telephone lines for transmission (local calls)., , — Another example of baseband transmission is computer data transmission over the coaxial cables in the computer networks., , — Thus the baseband transmission is the transmission of the original information signal as it is., , Limitations of baseband transmission :, , 1. The baseband transmission cannot be used with certain mediums, e.g. it cannot be used for the radio transmission where the medium, is free space., , 2. This is because the voice signal (in the electrical form) cannot travel long distance in air., , 3. It gets suppressed after a short distance. Therefore in order to accomplish the radio communication of baseband signals a technique, called modulation is used., , , , , , , , , 2.2 Basics of Modulation :, , DSS |, Q.1 Define modulation. (S-07, S-08, S-09, 2 Marks, S-13, 1 Mark), Q.2 Define modulation and explain need of modulation. (S-11, S-14, 4 Marks), 'Q:3 Define modulation, State the desirable value of modulation index of AM. (W-17, 2 Marks), , — In the Modulation process, two signals are used namely the modulating signal and the carrier., — The modulating signal is nothing but the baseband signal or information signal while carrier is a high frequency sinusoidal signal., , Modulating M, 1 jodulated, signal Modulator signal, , Carrler, signal, , S-07, S-08, S-09, S-11, S-13, S-14, W-17, , , , , , , , (-8) Fig. 2.2.1 : Modulation