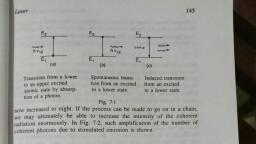
Page 1 :
(For Mathmatics Oe ;, 7 Mist iy, Home Science A :, , troduction, word * a3, , The Ps LASER’ 1s an acronym for Ligs, of Radiation. It is a device to produce a strone. , Amplification by Stimulated Emission, coherent mn oS light. It works on the phenomendia Ween collimated and highly, , The ingenious principle of | of “stimulated emission”., , 5 . a ‘aser was first, , mbia University. He _. otSt Worked out i ‘harles Townes of, Semler device, Reins use of this principle a few years clad 1953 to invent a, yery Ws The > Where microwaves are used inst af fli Hence (eer, js an OP els Te first Successful laser using a | ae light WAVES a, b Teodore H. Maimann in 1960, 8 a large synthetic ruby crystal was built, , The light pulse from a laser has the following characteristi, , ‘acteristics., , ( Laser light is highly monochromatic, e laser is a bez zZ c an, Th eam of monochromatic light because all photons in the laser light have, , ergy, hy = Ey — Bj. a ee hae frequency, v = (Ez — E,)/h and hence same wave, , Jength, A = he/ (£2 — EF)., (i) Laser light is highly coherent, , Since the emission of all photons are in phase, the laser beam is coherent., , (ii) Laser light is highly intense, The intensity of laser beam is very high because all the photons in the beam are, , coherent., (iy) Laser light is highly directional, A laser beam departs from strict parallelism only because of diffraction effects, determined by the wavelength of the laser and the diameter of the exit aperture. Light from, other sources can be made irito an approximately parallel beam by a lens or a mirror, but, eater than that for laser light., , , , the beam divergence is mucl, , Principle of Laser, Laser works on the simple principle of quantum theory of radiation. To understand, , the principle of the laser we must know the following terms., , —___—_e——-F,,, , (i) Absorption of radiation, , E,, , , , WwAS\SL>, gE E,, , absorption of photon, , Fig. |, , 145