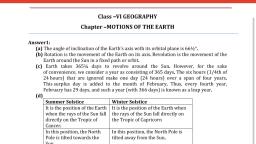
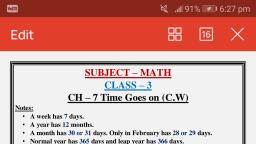
Page 1 :
3. The Earth rotates in a s, , —, , 4. Seasons occur due to the tilt o, , . Summer solstice is the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere occurring on, , 21 June. Winter solstice is the shortest day in the year. It occurs on 22 December in the, , Northern Hemisphere., , _ A year which has 366 days as a result of 4 day added every four years is called a leap, , year. The day on which the rays of the Sun fall on the Equator, resulting in equal lengths, of day and night, is called an equinox. There are 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of, night on such days. Equinoxes occur around 21 March and 23 September every year., , Summer is the season that occurs in the Northern Hemisphere when the North Pole is, , tilted towards the Sun, whereas autumn is the season when the two poles are at an equal, distance from the Sun. Summers are hot and autumn is pleasant., , . During the Earth’s rotation, the imaginary line that separates the illuminated part of the, , Earth from the dark part is called the circle of illumination., , The Earth takes one year or 36574 days to complete one revolution. However, we, consider one calendar year to have 365 days. The balance 4 day (or 6 hours) is added up, for four years in a row. This becomes an additional 24 hours or one day. Hence, once in, every four years, this extra day is added to the month of February. As a result, February, , has 29 days in that year, which is called a leap year. We have 366 days in a leap year., lightly slanted position as its axis is tilted. The direction of, , rotation is from west to east., £ the Earth’s axis as our planet revolves around the Sun., , , , , , , , , , , he tilt of the Earth also causes variations in the length of days and nights. During, 1, days are long and nights are short. In winter, it is the opp, rter, and it gets dark early. a, , mera