Page 1 :
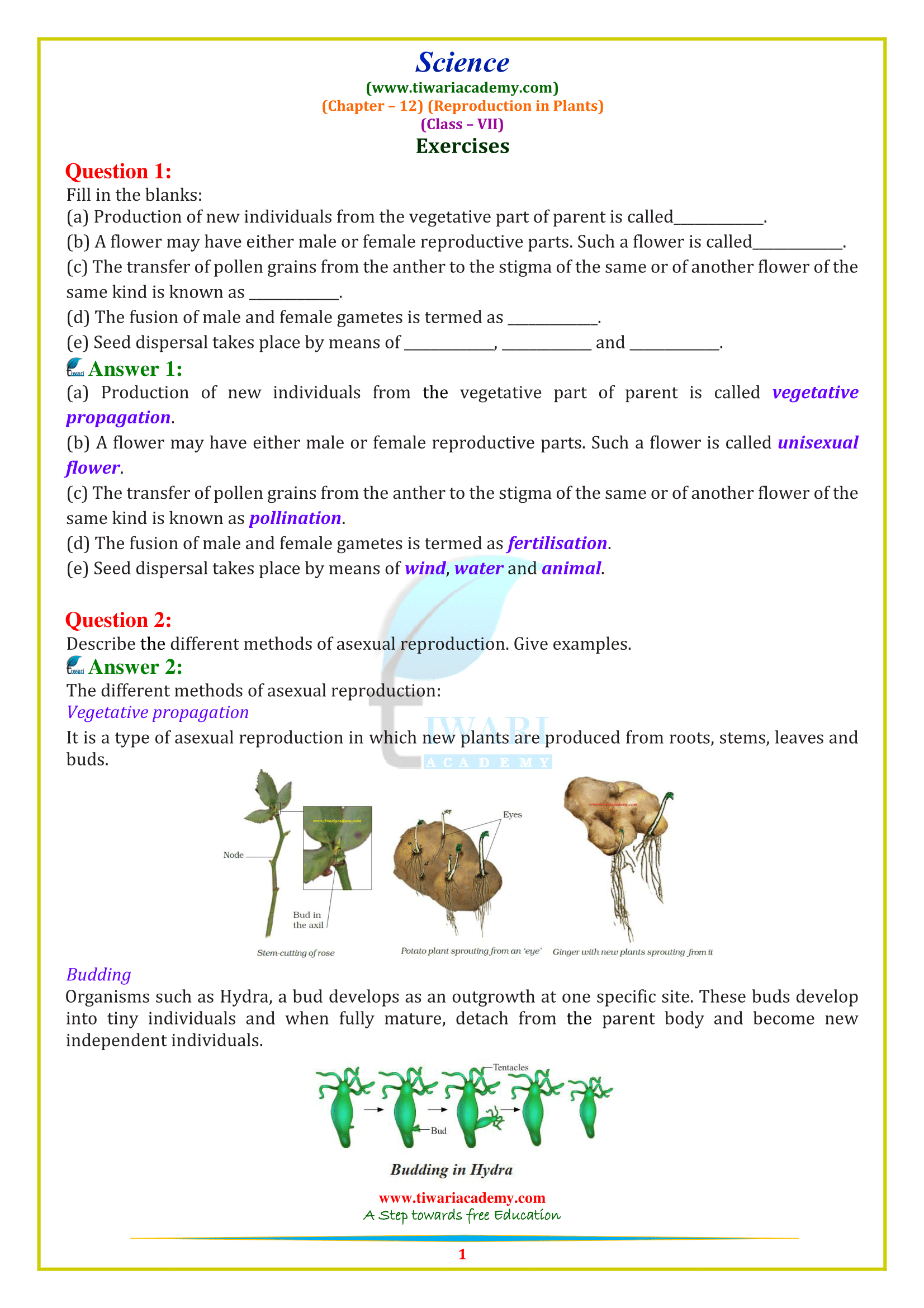
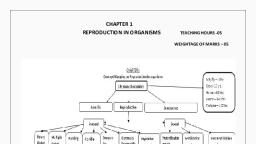
Science, , (www.tiwariacademy.com), (Chapter - 12) (Reproduction in Plants), (Class - VII), , Exercises, Question 1:, Fill in the blanks:, (a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called, (b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called, (c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the, same kind is known as ., (d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as, (e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of , and, €. Answer 1:, (a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative, propagation., (b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual, flower., (c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the, same kind is known as pollination., (d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation., (e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animal., , Question 2:, , Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples., , €. Answer 2:, , The different methods of asexual reproduction:, , Vegetative propagation, , It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and, buds., , }, , |, Bud in |, the axil |, , Stem-cutting of rose Potato plant sprouting from an ‘eye’ Ginger with new plants sprouting from it, , Budding, Organisms such as Hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth at one specific site. These buds develop, into tiny individuals and when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new, , independent individuals., ‘Tentacles, is ., , Budding in Hydra, , www.tiwariacademy.com, A Step towards free Education, , 1