Page 1 :
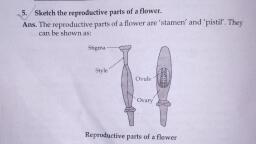
Chapter -12 Reproduction in plant, 2.,Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples., Ans. The various modes of asexual reproduction are as follows: Budding: Single-celled organisms such as yeast multiply by the process of budding. A small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is known as a bud. When the bud grows, it detaches itself from the parent body and forms a new individual. Fragmentation: Algae such as Spirogyra reproduces by the process of fragmentation. The filamentous algae breaks into two or more fragments and each fragment grows into a new individual. Spore formation: Plants like moss and ferns reproduce by means of spores. Spores are released into air. They are covered by a hard coat to protect them from conditions like high temperature and low humidity. Under favourable conditions, spores germinate to form new plants., 3.,Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction., Ans. In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds., 4.,State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction., Ans. In sexual reproduction, seed is required but in asexual reprodúcțion seed is not required., 6. Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination., Ans. If the pollen lands on the stigma of the same flowers it is called self-pollination. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of another flower of the same plant, or that of a different plant of the same kind, it is called cross-pollination., Q. 7. How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers ?, Ans. The cell which results after fusion of the gametes is called a zygote. The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilisation. The zygote develops into an embryo., Q. 8. Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed., Ans. Seeds and fruits of plants are carried away by wind, water and animals. Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple, light seeds of grasses or hairy seeds of aak (Madar) and hairy fruit of sunflower get blown off with the wind to far away places. Some seeds are dispersed by water. These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut. Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant place . Examples are Xanthium and Urena. Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks. The seeds are scattered far from the parent plant. This happens in the case of castor and balsam. .