Page 1 :
chaf>ter 15: Light, A., , Tick(✓), , the correct options., , 1. (d), B., , C., , 2. (d), , 3., , (c), , 4., , (a), , Fill in the blanks., 3. spectrum, 1. Convex, 2. focal length, 6. magnifying glasses, 5. Concave, 4. dispersion, 7. Concave, 8. convex mirror, State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F)., , 1. F, , 2. T, , 3. F, , 4., , F, , D. Very Short Answer Questions., 1. An image of a boy in the plane mirror., 2. Concave lens, 3. Real image, 4. Bulging surface always forms an erect image., 5. Concave lens, 6. Convex mirror, E., , Short Answer Type-I Questions., 1., , The process of sending back the light rays which fall on the surface of an, object is called the reflection of light., , 2., , A lens is a piece of transparent materials (glass or transparent plastic), bound by two curved surface or by one curved and one plane surface., , 3., , S.No., , 1., , Convex lens, , Concave lens, , The convex lens is thicker The concave lens is thinner in the, in the middle and thinner middle and thicker at the edges., at the edges.
Page 2 :
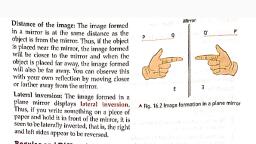
F., , 2., , It is a converging lens., , It is a diverging lens., , 3., , It has a real focus., , It has a virtual focus., , 4., , The principal focus of a spherical lens is the point on the principal axis, where all the light rays which are parallel to the principal axis meet or, appear to meet., , 5., , (a) Convex lens, , (b) Concave lens, , Short Answer Type-II Questions., 1., , The image formed in plane mirror is, (i) of the same size and shape of the object., (ii) virtual and erect., (iii) laterally inverted with respect to the object., (iv) at the same distance from the mirror as the object., , 2., , Light enables us to see the objects around us. When light after reflection, enters our eyes, we are able to see the objects. When light falls on the, surface of an object, the object sends the light back. This process of, sending back of light rays which fall on the surface of an object is called, reflection of light., , 3., , The image which can be obtained on a screen is called a real image. A, real image is always inverted. It is formed on the same side of the mirror, where the object is placed., The image which cannot be obtained on a screen is called a virtual, image. It is always erect. It is always formed behind the mirror., , 4., , Newton with the help of Newton's disc demonstrated that all seven, colours together makes a white light., , 5., , Concave mirrors are, (i), , used as shaving mirror., , (ii) used as reflectors in torches and headlights of vehicles., (iii) used by dentist to see enlarged image of teeth., G., , Long Answer Questions., , 1., , (a) F and F' are the focus of a convex lens., (b) 0 is the optical centre of convex lens., (c) distance between O and F or the distance between O and F' is the, focal length of convex lens., , 2F, , F, , p, , 2P
Page 3 :
2., , (a) The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its component, colours on passing through a transparent medium like glass prism, is called dispersion of light., p, , {b), , ~o~, ~ue,1> X'b'(-.\, , w hite screen, , B, , R, 0, y, , ·\e,, , ~'(\\, , ~\, , A, , ', , o/, Q, , 1,_c,\,)(\\,~ Wb'(-., , 0~, , 'o\,)\'o, , ~r, , Ol'AOI\<', , G, , rr'"", , V, , \'lo,k,c, , 9, I, , r, , 1.-llow C, , r, "", R, ond•JII), u, M, , R, G lass prism, , A glass prism splits the white light into seven colours., (c) Rainbow formation after the rain.