Page 1 :
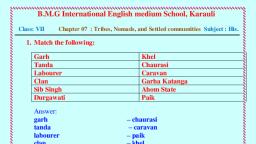
Chapter – 07 History, Tribes, Nomads and Settled Communities, •, , During the Medieval Age, several social, economic and political development took place., , •, , The Indian society was divided on the basis varnas. During the medieval period, gap between, the rich and poor increased., , •, , There were, however, several communities which did not follow rules laid down by the, Brahmins. Thesej included the tribes, nomads and settled communities., , •, , Tribal Societies:, (i), , Tribes are people who do not follow norms laid down by society., , (ii), , Most of the tribes were dependant on agriculture. Others were herders or huntergatherers., , (iii), , Tribers were even nomadic and moved from one place to another., , (iv), , There were even clashes between tribes and powerful caste-based societies., , (v), , Contemporary historians and travelers from medieval India hardly give any, information about the tribes., , (vi), , Some of the powerful tribes were Khokhar tribe in Punjab; Langahs and Arghuns in, Multan; Gaddis in the Himalayas; Kolis and Berads of Gujarat; Gonds of Chhattisgarh,, Bhil tribe in Central India, etc., , •, , Pastoral Nomads:, (i), , The pastoral nomads moved from one place to another with their herd of animals., , (ii), , They survived on milk products and exchanged ghee, wool, etc. with farmers for, grains, cloth, utensils, etc., , (iii), , The most important trader nomads were Banjaras. Their caravan was called ‘tanda’., Sultan Alauddin Khalji used Banjaras to move grain to the city markets., , (iv), , Pastoral tribes thus, basically reared and sold animals like horses and cattle to the, prosperous people., , •, , Changes in Caste Structure of India:, (i), , In the fields of trade and agriculture, there emerged multi-caste population in many, villages on account of the spread of Islam., , (ii), , Sufi and Bhakti movement preached equality between different castes and religious, groups.
Page 2 :
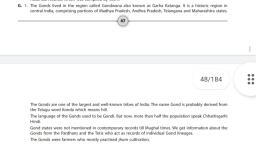
•, , (iii), , Inter-caste marriages started between Rajputs and Muslim nobles., , (iv), , With the growth of economy, new jatis and varnas emerged., , (v), , Many tribes became part of ruling changes., , The Gonds:, (i), , Gonds were sometimes referred to by their tribal dialect, Gondi. They practice shifting, cultivation., , (ii), , The Gonds rose when Delhi Sultanate declined., , (iii), , The Gond kingdom is Gondwana in southeastern Madhya Pradesh was found in the, 15th century., , •, , Ahoms:, (i), , The Ahom tribe is traced to some tribes living in south-east Asia who had travelled, over land through the forests of Assam., , (ii), , The religion and culture of Assam is a fusion of the local traditions and of migrant, tribes., , (iii), , The Ahoms belonged to a warrior class and built roads and irrigation system even, before establishing their rule., , (iv), , The Ahoms formed the new kingdom by suppressing the older political system of, Bhuiyans.