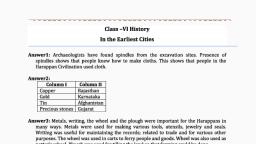
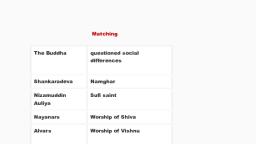
Page 1 :
Chapter – 08 History, Devotional Paths to the Divine, •, •, , •, , •, , •, , •, , •, , •, , Intense devotion or love of God is the legacy of various kinds of Bhakti and Sufi movements, that have evolved since the 8th century., The Idea of a Supreme God:, (i), Before large kingdoms emerged, different groups of people worshipped their own, Gods and Goddesses. As people were brought together through the growth of towns,, trade and empires, new ideas began to develop., (ii), The idea that all human-beings are not equal at birth gained ground during this, period., (iii) The idea of a Supreme God who could deliver humans from bondage through devotion, or bhakti emerged., (iv) Gods and goddesses worshipped in different areas came to be identified with Shiva,, Vishnu or Durga., A New kind of Bhakti in South India- Nayanars and Alvars, (i), The seventh to ninth centuries saw the emergence of new religious movement, led by, Nayanars (saint devoted to Shiva) and Alvars (saints devoted to Vishnu)., (ii), They were sharply critical of the Buddhists and Jainas and preached ardent love of, Shiva or Vishnu as the path to salvation., (iii) The Nayanars and Alvars went from place to place composing exquisite poems of, praise of the deities enshrined in the village they visited, and set them to music., (iv) The Chola and Pandya kings built elaborate temples around many of the shrines., Philosophy and Bhakti:, (i), Shankara, a philosopher, of Kerala advocated Advaita or the doctrine of the oneness of, the individual soul of the Supreme God which is the ultimate reality., (ii), Ramanuja of Tamil Nadu advocated that the best means of attaining salavation was, through intense devotion to Vishnu., Basavanna’s Virashaivism:, (i), Virashaivism movement was initiated by Basavanna and his companions Allama, Prabhu and Akkamahadevi in Karnataka in mid-12 century., (ii), They argued strongly for equality of all human beings, opposed Brahmanical ideas on, caste and treatment of women., The Saints of Maharashtra:, (i), Jnaneshwar, Namdev, Eknath, Tukaram, Sakkubal and the family of Chokhamela, focused on the bhakti of Vitthala (a form of Vishnu)., (ii), Some of these belonged to lower castes. They rejected all forms of ritualism, outward, display of piety and social differences based on birth., Nathpanthis, Siddhas and Yodis:, (i), A number of religious groups that emerged during this period criticized the ritual and, other aspects of conventional religion and the social order, using simple, logical, arguments., (ii), Among them were the Nathpanthis, Siddhcharas and Yogis., Islam and Sufism:, (i), Islam propagated monotheism or submission to one God., It also rejected idol worship. Muslim scholars developed a holy law called Shariat., (ii)