Page 1 :
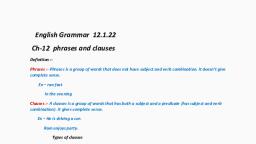
A clause is a sentence which is the part of a larger sentence. The lar, , complex or a compound sentence. Each large sentence must have two or, sentences must be a clause., , Ger sentence can be a, more sentences. These, , How can we judge whether it is a phrase or a clause?, Read the sentences given below :, , (i) Deepak is a boy who has a white shirt., (ii) Deepak is a boy with a white shirt., , When we see in sentence (i), there are two sentences joined by who, a conjunction. Both, sentences Deepak is a boy and who has a white shirt are clauses, because both the sentences are, complete sentences giving complete sense. But in sentence (ii), it is one sentence in which with a, , white shirt is a group of words without verb and does not have a subject or a predicate, so it is a, phrase and not a clause., , Definition : A group of words which has a subject and a predicate and which forms a part of, the larger sentence is called a clause., , KINDS OF CLAUSES, , Before going to read the kinds of clauses, we must recall our memory what we have studied, about the sentence and its kinds because these sentences formulate the clauses., , Sentences : (a) Simple Sentence. (b) Complex Sentence. (c) Compound Sentence., (a) Simple Sentence : It contains a verb, so the question of clause does not arise., , (b) Complex Sentence : A sentence which contains two or more than two sentences duly, connected by a conjunction, is a complex sentence. It contains a main or a principal clause and, _ other clauses are called subordinate clauses.
Page 2 :
(c) Compound Sentence : A sentence con, the conjunctions ‘and’, ‘yet’ or ‘but’ js called a co, , than two clauses. The clause without conjunctions ‘and’, ‘yet’ and ‘but’ is a main or a principal clause, and the clause beginning with conjunctions is called co-ordinate clause., , F Given below are the kinds of clauses | 1. Principal Clause, , , , : 3 eas, 7 It is a main sentence or the clause whi, the beginning of the sentence, but it somet;, , the complex sentence, if it is taken off, the meaning of other clauses cannot be cleared. So, it is the, , main sentence or clause in respect of a complex sentence., , But, in a compound sentence, if it is taken off,, remaining clause will be clear. This clause is without, to a clause, it becomes either a subordinate or Co, , it does not matter because the meaning of the, , any conjunction. When any conjunction is added, -ordinate clause., , Read the following sentences to Get a clear view about the main clause (i) I was coming out of the house when he came., (ii) The pen, which I bought, is lost., , Here, in sentence (i), I was comin, beginning of the sentence, but in the ca, the beginning and the rest is in the end., , 2. Noun Clause, , Q out of the house is the main clause mostly used in the, se of sentence (ii), a part of the main or principal clause is in, , lf the answer to what of main clause lies in the subordinate clause, it must be a noun clause., Now read the following sentences :, , (i) She said that she would come to see me. (ii) I do not know when he will come., , In sentence (i), She said (what she said) that she would come to see me. It contains a subject (she), and a Predicate (would come to see me). So, it is a noun clause., , In sentence (ii), | do not know (what) when he will come is.also a noun clause., , A noun clause is a group of words which contains a subject and a predicate of its own and does, the work of a noun., , 3. Adjective Clause, , Read the following sentence :, , The pen, which you gave me, was lost., , In the above sentence, the group of words, which you gave me qualifies the noun ‘the pen’ and, does the work of an adjective. But it contains a subject and a predicate of its own, it is called an, adjective clause., , An adjective clause is a group of words which contains a subject and a predicate of its own,, , and does the work of an adjective., 4. Adverb Clause, , Read the following sentence :, , I do not know wh he was late. : |, In the above ates the group of words, why he was late is a clause, as it has a ee (he), and a Predicate (late) of iis own. But it does the work of an adverb, it is called an adverb clause., , + ae Se
Page 3 :
An adverb clause is a group of words which contains a subject and a predicate of its Own, and, does the work of an adverb., , 5. Co-ordinate Clause, , A co-ordinate clause does not depend upon the main clause for its meaning like a subordinate, clause. These clauses are followed by and are joined with the main clause with conjunction. But they, are thought to be separate as, in the absence of main clause, its meaning is clear, e.g. ,, , (i) He went to the market and purchased a book., (ii) He is rich but he is a miser., , In the above sentences, and purchased a book and but he is a miser are co-ordinate clause,, because they do not depend upon the main clause for their meaning.