Page 1 :
C8, Physics, Stars and The Solar system., 1. What is a Celestial body?, A naturally occurring physical object in the cosmos, outside the earth’s, atmosphere, is called a celestial body., The planets, the stars, the moon, and other bodies in the sky are known as, celestial bodies., , 2. What is Astronomy?, It is a branch of science that studies celestial bodies and the, associated phenomena., 3. Differentiate full moon day and a new moon day., Full moon day, New moon day, The day on which the whole disc, of the moon is visible is known as, the full moon day., , The day on which the moon is not, visible is known as the new moon, day., , 4. Explain the different phases of the moon with a neat diagram., • Various shapes of the bright part of the moon seen during a month are, known as the phases of the moon., • The phases of the moon occur as we can only see the part of the moon, that reflects the light of the Sun towards us.
Page 2 :
• The moon does not produce its own light but reflects the light of the, Sun. As the moon revolves around the earth, different parts of its, surface get illuminated and we see a different shape every day., • The cycle is about 29 days, where it goes from a full moon to a new, moon to a full moon., , 5. We never see the back (dark) side of the Moon. Why?, •, , •, , The part of the moon that always faces away from the earth is called, the dark side of the moon., The moon’s time period for rotation on its axis and revolution around, the earth is approximately the same. (≈ 27.3 days). Therefore an, observer always sees the same face of the moon from earth., , 6. Describe the surface of the Moon., •, , The surface of the moon is barren and dusty and devoid of water. It has, many large craters and high mountains., Note:, The moon’s gravity is 6 times weaker than the earth’s. It does not have, any atmosphere. That is why we cannot hear on the surface of the, moon., , 7. Write a short note on stars., •, , •, , Stars are celestial bodies that emit their own light and heat. Our sun is, an example of a star., Although stars are always present in the sky but are only visible at night, due to the absence of sunlight.
Page 3 :
•, , •, , They appear as points as they are millions of kilometers away from us., Stars twinkle as their light gets refracted in our atmosphere., The position of stars keeps changing as seen from the earth’s surface,, apart from the Polestar whose position is fixed., , 8. What is a pole star? Which constellation helps us to locate it?, •, , •, , The Pole star (or Polaris) is one star whose position seems to be fixed. All, other stars seem to move around the Pole Star., It can be traced using the constellation Ursa Major., , 9. Define a light year., •, , •, •, •, •, , The distance traveled by light in one year is called a light-year. It is a, measure of distance for celestial objects, Note:, Speed of light = 3 X 108 m/s, 1 light-year = 9.46 X 1012 km, The sun is 8 light minutes away from earth., The distance of Alpha Centauri is 4.3 light-years away., , 10. What are Constellations? Give examples., •, , •, , A group of stars that form a recognisable shape in the night sky is called, a constellation. They were devised by ancient men for navigation, purposes., Examples: Ursa major (Great bear), Orion, Leo major
Page 4 :
11.Describe our solar system briefly., •, , •, , The sun and all other planets and celestial bodies that revolve around it, are together called a solar system. Our solar system has 8 planets and, an asteroid belt. Pluto is considered as a dwarf planet., All planets in the solar system revolve around the sun in fixed orbits., Planets nearer to the sun revolve faster as compared to the planets, away from the sun., , The Sun, •, , •, , The sun is the nearest star to earth. It is continuously emitting heat and, light., It is the main source of heat and light energy for all planets in our solar, system., , The Planets, •, •, , •, •, , Planets are celestial bodies that do not emit heat or light of their own., They revolve around a star in fixed paths called orbits and the time it, takes to go around the sun once is known as its period of revolution., A planet also spins on its own axis which is called a rotation., Orbit is a fixed path that a planet takes to revolve around the sun.
Page 5 :
Mercury (Budh), •, , •, , •, , Mercury is the nearest planet to the sun and also the smallest planet in, our solar system., It is usually hidden due to the sun’s glare but can be seen just before, sunrise or after sunset., Mercury has no satellite of its own., , Venus (Shukra), •, •, •, , •, •, , Venus is the brightest planet in the night sky., It is the closest planet to earth., Although not a star, it is called the morning star or evening star as it, appears in the eastern sky before sunrise and in the western sky after, sunset., Venus has no satellite of its own., Venus rotates from east to west while the earth rotates from west to, east on its orbit., , The Earth (Prithvi), •, , •, , •, •, , The earth is the only habitable planet in our solar system. Life exists on, earth due to several optimal conditions like the presence of, atmosphere and water and the right distance away from the sun., The earth appears bluish-green from outer space as the light from the, landmass and water bodies gets reflected., Earth has only one natural satellite: the Moon., The earth’s axis of rotation is tilted which causes seasonal variations., , Mars (Mangal), •, , •, , Mars is the 4th planet from the sun. It is often referred to as the “Red, Planet” because the reddish iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it, a reddish appearance., Mars has 2 natural satellites.
Page 6 :
Jupiter (Brihaspathi), •, , •, , •, , Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. So big, that it can, accommodate 1300 earths. Although it is only 318 times heavier than, earth., Jupiter has 53 named moons and another 26 awaiting official names., Combined, scientists now think Jupiter has 79 moons., Jupiter has a big red spot which is a gigantic storm that has been, swirling for many years which is twice as wide as earth., , Asteroids, •, , •, •, , Asteroids are a large number of small celestial objects between the, orbits of Mars and Jupiter., They revolve around the sun too in their orbit., Asteroids together form a belt., , Saturn (Shani), •, , •, •, , Saturn is the second-largest planet in our solar system. It is unique as it, has thousands of beautiful rings., Saturn has a large number of moons., Saturn is the least dense among all the planets its density is less than, that of water., , Uranus and Neptune, •, , •, , Uranus rotates from west to east. Its axis has a huge tilt which makes it, look like it's spinning on its side., Neptune is the 8th and farthest planet in our solar system. It has really, strong winds which are more powerful than any other planet in the solar, system., , Comets, •, , •, , Comets are celestial bodies that revolve around the sun in long, elliptical orbits. They are usually made up of ice, dust, and gasses and, have a very long tail that is always directed away from the sun., As a comet gets closer to the sun, it heats up and spews out jets of gas,, and forms a huge glowing head.
Page 7 :
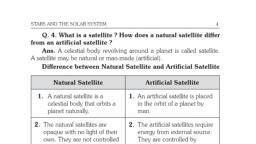
Meteors and Meteorites, •, , •, , •, , Meteors are small objects mainly leftover broken asteroids that enter, the earth’s atmosphere at high speeds., The friction between the atmosphere and the meteor causes it to burn, and evaporate before it reaches the surface. That is why they appear, as bright streaks of light in the sky., Sometimes when a meteor is large and does not evaporate in the, atmosphere, it strikes the surface. This is known as a meteorite., , 11.What are artificial satellites? Give examples., •, , •, , •, , Artificial satellites are man-made objects that are launched from earth, and revolve around the earth much closer than natural satellites., They are used for various applications like remote sensing, weather, forecasting, transmitting signals., Examples: INSAT, IRS, Sputnik -1, , 12. Explain how you can locate the pole star with the help of Ursa Major., To locate the Pole star in the sky, first of all, Ursa Major or Big dipper, constellation must be located. The bowl of big dipper consists of four bright, stars as shown in the figure.
Page 8 :
Consider two stars at the end of this bowl. Now, draw an imaginary, straight line towards the Northern direction connecting these two stars, as shown in the figure., , This imaginary line meets a star called the Polar star. The length of the, imaginary line from the bowl is about five times the distance between the, two stars of the bowl.
Page 9 :
13. Do all the stars in the sky move? Explain., No, the earth rotates from west to east on its axis. Hence, all stars in the sky, (except the pole star) appear to move from east to west. With reference, to the earth, the pole star does not appear to move in the sky because it is, located above the axis of the earth’s rotation in the north direction., 14. Why is the distance between stars expressed in light years? What do you, understand by the statement that a star is eight light-years away from the, earth?, It is inconvenient to express the distance between the stars and the earth, in kilometers because these distances are quite large so, they are, expressed using a big unit called light-years., One light year = 9.46 X 1012 km, A star located eight light-years away from the earth means that the, distance between the star and the earth is equal to the distance traveled, by light in eight years, i.e., a star is located, 8 X 9.46 X 1012 km = 7.6 X 1013 km away from the earth., 15. The radius of Jupiter is 11 times the radius of the Earth. Calculate the ratio, of the volumes of Jupiter and the Earth. How many Earths can Jupiter, accommodate?