Page 1 :
Kerala Class 8 BS, , Simplified Notes, English Medium, All Units, Units :, , 1. Life's Mysteries in Little Chambers, 2. Cell Clusters, 3. Let's Regain our Fields, 4. Why Classification ?, 5. Diversity for Sustenance, 6. For the Continuity of Generations, Prepared by, , Rasheed Odakkal, , 2021, Copyleft
Page 2 :
Class 8 - BS Unit 1 (Biology 1), , 1. Life's Mysteries in Little Chambers, * The body of all organisms are made up of cells ., * Microscope is used to observe the cells., * Microscopes in which more than one lens is used are called compound microscopes ., A compound microscope magnifies an object only 2000 times (maximum) its size., While electron microscopes, which utilize electrons instead of a light source, can, magnify objects million times clearly., * Parts of a compound microscope :, Electron microscope, Eyepiece, , Knobs, Objective lens, Stage and clip, Condenser, Mirror, * Eyepiece and Objective lens are the two types of lenses, seen in a compound microscope., * The lens in the condenser focuses light on the material to be observed ., Diaphragm of the condenser helps to regulate the intensity of light., * Mirror is with a plane mirror on one side and a concave mirror on the other side., * Stages for the preparation of the observation material (for instance, a cross section of, plantain root), 1. Put the material in water (to prevent dehydration), 2. Take thin sections of the material and keep it in a watch glass containing water., 3. Put the thinnest complete sections to a watch glass containing stain., (to get colour to cells), 4. Add one or two drops of glycerin to the slide. (to prevent the drying up), 5. Wash one of the stained sections and place it in the glycerin on the slide., 6. By using a needle, place a cover glass over it without forming air bubbles., 7. By using a tissue paper, wipe out the excess glycerin., 8. Place the slide and observe it through the microscope., * Milestones in the history of Cell Biology) :, 1665 Robert Hooke, Observed cells with the help of a simple microscope., He called the tiny chambers, as “cells”., 1831 Robert Brown, , Discovered and named the centreof cell, 'Nucleus', , 1838 M.J.Schleiden, , Found out that the body of plant is made up of cells., , 1839 Theodor Schwann Found out that an animal's body is made up of cells., 1858 Rudolf Virchow, , Observed dividing cells and inferred that new cells, arise only from existing cells
Page 3 :
* The cell theory :- (formulated by M.J Schleiden and Theodor Schwann ), 1. The body of all organisms is made up of cells., 2. Cells are the structural and functional units of organisms., * Functions performed by the cells :- Resist foreign particles ,, - Release energy from nutrients ,, - Synthesise biomolecules ., * The covering of a cell ?, Cell membrane (plasma membrane), * Why plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane ?, As they allow only the essential materials to pass., * Protoplasm ?, All substances inside the cell membrane (Cytoplasm + Nucleus = protoplasm ), * The controlling centre of a cell ? Nucleus., * Prokaryotes are organisms with out a nucleus in their cell., (eg:- Bacteria, Cyanobacteria, Mycoplasma), Eukaryotes are organisms with a well defined nucleus in their cell., (eg:- Amoeba, Animals, Plants), * Parts of a nucleus :Nuclear membrane Double layered covering, Nuclear pore, , Pores in the nuclear membrane, , Nucleoplasm, , Fluid part of nucleus, , Nucleolus, , Spherical bodies, that help in, ribosome synthesis, , Chromatin, reticulum, , Gene carrying network in the, nucleoplasm, , * Cell organelles ? Specific parts seen in the cytoplasm., Cell organelles seen in both the plant and animal cells :- Mitochondrion,, Endoplasmic reticulum, Ribosome and Golgi complex., Cell organelles seen only in plant cells :- Vacuole and Plastids., Cell organelles seen only in animal cells :- Centrosome and Lysosome., Cell wall, Cell membrane, (plasma membrane), , Nucleus, Centrosome, Endoplasmic reticulum, Mitochondrion, , Vacuole, , Golgi complex, Lysosome, Chloroplast, PLANT CELL, , - Cellwall is present, - Vacuole and Plastids present, - No Centrosome and Lysosome, , Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, ANIMAL CELL, , - No cellwall, - No Vacuole and Plastids, - Centrosome and Lysosome seen, , Plasma membrane, Nucleus, Mitochondrion , Endoplasmic reticulum,, Ribosome, Golgi complex are seen in plant and animal cells
Page 4 :
* Different types of cell organelles and their functions :Cell organelle, , Function, , Mitochondrion, , Peculiarity, , Production and storage, Abundantly seen in the cells of, of energy, liver, brain and muscles, (Power house of the cell), , Endoplasmic reticulum Conduction of materials (The passage in the cell), Provides firmness and shape to the cell. (Cytoskeleton), Ribosome, , Protein synthesis, , Seenattached to the endoplasmic, reticulum or free in the cytoplasm, , Golgi, complex, , Collects cell secretions, like enzymes, hormones,, mucous etc., in small, vesicles., , Seen in plenty in glandular cells., , Vacuole, , Stores water, salts,, excretory materials etc., , Its membrane is called tonoplast., , Plastids, * Chromoplast, * Chloroplast, * Leucoplast, , - Impart colours to flowers and fruits., - Performs photosynthesis, Gives green colour to plant parts, - (no specific colour) Seen abundant in storage cells., , Centrosome, , Contains the centrioles, that helps in cell division., , Lysosome, , Contains digestive enzymes, that destroy foreign, substances entered in to the cell., Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, , * Examples for pigments presented in different chromoplasts :- Xanthophyll (yellow),, - Carotene (yellowish orange),, - Anthocyanin (red, purple)., * Pigment seen in the chloroplast ?, - Chlorophyll (green)., * The secret behind the change in the colour and taste of fruits ?, As fruits ripen, chloroplasts change to chromoplasts, to change its green colour., Starch in the fruits is converted to sugar, to change its taste., Plant cell, Cell wall, , Animal cell, , Plasma membrane, , Protoplasm, , Cytoplasm, , Nucleus, , Cell organelles, - Mitochondrion, - Endoplasmic reticulum, - Ribosome, - Golgi complex, - Vacuole, - Plastids, , Plasma membrane, Cytoplasm, , Protoplasm, Nucleus, , Cell organelles, - Mitochondrion, - Endoplasmic reticulum, - Ribosome, - Golgi complex, - Centrosome, - Lysosome
Page 5 :
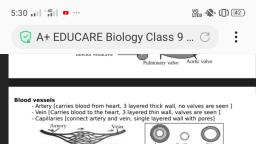
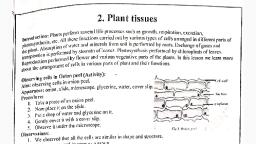
Class 8 - BS Unit 2 (Biology 2), , 2. Cell Clusters, * Human body is made up of millions of different kinds of cells like nerve cells, muscle, cells, blood cells and bone cells., * Tissues :- Groups of similar cells that have a common origin and perform specific, functions., * Animal tissues :- Epithelial tissue, Nervous tissue, Muscular tissue and Connective, tissues (blood, fibrous tissue, Cartilage, bone etc.), * Plant tissues :- Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma and Vascular tissues (xylem, and phloem), * Animal tissues are developed from a single undifferentiated cell, called the zygote., * Plant tissues are developed from rapidly dividing cells, called the meristematic cells., * Cell differentiation :- The process by which all tissues are developed from a single cell., [eg:- The formation of animal or plant tissues after continuous division and changes], zygote, , Foetal cells, , Nerve cells, Bone cells, Muscle cells, Blood cells, Meristematic tissue, , Meristematic cell, , Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma, Xylem, Phloem, , * Stem cells :- specialized cells that can transform into any kind of cells through constant, differentiation. Stem cells are found in the bone marrow, skin, digestive tract etc., * Importance of stem cells ?, The research of stem cells can bring about miraculous changes in the treatment of, blood cancer, diabetes, parkinson disease etc., and also in the manufacture of, artificial organs., * Meristematic tissue :- Specific cells seen at the tip of the stem or root in plants. They, undergo rapid division, which results in the growth of plants., * Comparison between a meristematic cell and a mature plant cell,, Meristematic cell, , -, , Rapidly dividing cell, Relatively large nucleus, Thin primary cell wall, More cytoplasm, No vacuoles, , * Tissues , Function and peculiarities., Animal tissues, , 1. Epithelial tissue, - Functions such as, protection, absorption, and cell secretions., 2. Nervous tissue, - Controls and coordinates, physiological functions and, responds to identify changes, inside and outside the body., , Mature plant cell, , -, , No further growth by division, Relatively small nucleus, Thick secondary cell wall, Less cytoplasm, Large vacuole, , Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, Plant tissues, , 1. Parenchyma, - Composed simplest cells., - Seen in the soft parts., - Helps in photosynthesis and, the storage of food., 2. Collenchyma, - Composed of cells that are, thick only at the corners of, the cell wall.
Page 6 :
3. Muscular tissue, - Consists of cells that can, contract and regain the, original state., - Enables the movement of, the body., 4. Connective tissue, , - Provides flexibility and support to plant, parts., 3. Sclerenchyma, - Composed of cells that are, uniformly thick all over the cell, wall., - Provides strength and support to plant, parts., 4.Vascular tissues, a. Xylem : Tubes formed from, elongated cells, with thick wall., - Transports water and minerals, a.Bone, Provide support, protection absorbed by the roots to the, b.Cartilage and a definite shape., leaves., - Provides support and strength., c.Fibrous tissue :- Connects other, b.Phloem: Composed of tubular, tissues., inter-connected cells., d.Blood :-Coduction of materials and, - Transports food from leaves to, resistance of the body., various parts of theplant body., , * Why are the vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) known as 'complex tissues' ?, Because they are formed from different kinds of cells., * Comparison between xylem and phloem., Xylem, , Phloem, , - Conduction of water and minerals from roots. - Conduction of food from leaves., - Cells with thick wall., - Relatively thin cell wall., - Provides support and strength to plant body. - Inter-connected tubular cells., Both are vascular tissues for conduction of materials, Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, , *, , Cells combine to form tissues., Tissues combine to form organs., Organs combine to form organ systems., Organ systems combine to form organism., [eg;- Digestive system is comprised of organs like stomach, intestines and liver., These organs are, in turn, formed by epithelial tissue, nervous tissue,, muscular tissue and connective tissues. All tissues are formed by cells], Cells, , Tissues, , Organs, , Organ systems, , Organism, Population, , Community
Page 7 :
Class 8 - BS Unit 3 (Biology 3), , 3. Let's Regain our Fields, * Food security is the situation that ensures sufficient food for everyone to lead a healthy life ., * The crises or obstacles faced by farmers today,, - High cost of production, - Fall in price of products, - Exploitation of middle people, - Climate change, - Lack of space, - Environmental destruction, - Crop loss, - Lack of interest, - Diseases, * How can we overcome certain issues in the field of farming ?, - Increase the fertility of soil scientifically., - Proper testing the soil., - Proper irrigation, - High yielding hybrid varieties, - Controlling disease, - Agricultural socities, - Integrated pest management, - Organic waste management, - Adopt modern agricultural practices like hydroponics, polyhouse farming, precision farming etc., - Vertical farming, Terrace cultivation etc., * Methods for improving soil fertility ?, Organisms like bacteria, fungi, algae,termites, earthworms, leguminous plants etc increase fertility of, soil., Maintain the pH of soil by proper soil test and scientific application of fertilizers., * Examples for essential elements for plant growth ?, - C, H, O,N, P, K, and S, * Microbes that provide fertilizers ?, Bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter, Azospirillum, * Aquatic plants that provide nitrogen to soil ?, - Azolla, * Consiquences of uncientific application of chemical fertilizers ?, - Adversely affect the growth of microorganisms, - Health issues, - Change in the composition of soil., * What do you mean by Integrated pest management ?, - An ecofriendly method ensures pest control without disturbing the environment., This is done by reducing the use of chemical pesticides and encouraging the application of biopesticides,, natural enemies of pests, mechanical pest control etc., * Consiquences of excessive application of chemical pesticides ?, Possibility of many environmental and health issues. (eg:- cancer), * Methods for the disposal of organic wastes ?, - Composting, biogas production, production of fodder fish feed or poultry fodder., * Diversity in farming or culture:, , Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, , Sector, , Product, , Varieties, , Livestock management, (rearing of cattle), , Milk, Meat, Cow: Jersey, Holstein Friesian, Vechoor, (Also for agricul- Buffalo: Murrah, Niliravi, Bhadawari., tural purposes), Goat: Thalassery, Jamnapari, Boer ., , Poultry farming, (rearing of birds), , Egg, Meat, , Chicken : Athulya, Gramalekshmi,, White Leghorn, Duck : Muscovy, Chara, Chemballi, Quill : Japanese, Bob white., , Sericulture, (rearing of silkworms), , Natural silk, , Mulberry silkworm, Tussar silkworm,, Muga silkworm, , Pisciculture, (rearing of fish, prawn), , Meat, , Edible fish : Pearl spot, Rohu, Catla ., Ornamental fish : Gold fish, Guppy., Prawn: Naran, Kara., , Floriculture, (cultivation of flowering, plants), , Flowers, , Jasmine, Marigold, Chrysanthemum,, Rose, Orchid, Anthurium
Page 8 :
Apiculture, (rearing of honey bees), , Honey, Wax, , Kolan, Mellifera, Njodiyan, , Cuniculture, (rearing of rabbits), , Meat, Fur, , Grey giant, White giant (for meat), Ankora (for fur), , Mushroom culture, , Food, , Button mushroom (Palkoon),, Oyster mushroom (Chippikoon), , Horticulture, (cultivation of fruits and, vegetables), , Fruits, Vegetables Indigenous varieties and exotic varieties, like Litchi, Rambutan, Durian, , Medicinal plant cultivation, , Medicine, , Basil, Aloe, Neem, Adathoda, Sida, (Kurunthotti), Vettivera (Ramacham),, Aegle marmelos (Koovalam), Plumbago, (Koduveli), , * Examples for indigenous varieties of plants and animals :, Indigenous varieities can survive the challenges of adverse climatic conditions., Eg:- Mango : Muvandan , Kilichundan ., Plantain : Njalipoovan, Palayamkodan., Cow : Vechoor, Kasaragod Kullan ., Goat : Malabari, Attappadi black ., * Examples for a few techniques in farming (modern agricultural practices):, a)- Polyhouse Farming :- The crop field is completely or partially covered by transparent polyethene, sheets. Since the temperature and moisture in the polyhouse is constantly regulated, growth of, plants becomes rapid. Nutrients are dissolved in water and are supplied on plants through drip, irrigation. Pest infestation will also be less ., b)- Precision farming:- The nature of soil, quantity of elements in the soil, pH value of soil, presence of, water etc., are tested using modern technology, and appropriate crops are selected for cultivation., By covering the soil using polythene sheet, we can effectively control weeds and also limit, irrigation., c)- Hydroponics:-Plants are grown in nutrient solution., d)- Aeroponics:- Plants are grown in such a way that their roots grow into air and nutrients are sprayed, directly, on roots., * Importance of Agricultural Societies or Organizations:, - Helpful to farmers to market their products without the help of mediators and there by get maximum, price to their products., - The facility for storage of items is also ensured along with marketing facilities., - They can sell such stored products when prices are high in the market and make profit., - Loans at low interest rates are also made available to them., - The online organizations of farmers help to identify customers for their quality organic products and, ensure higher prices. Also possibilities to share their knowledge and experiences., * A real farmer should be, in fact, a scientist. Why ?, The farmer is one who applies the scientific methods like observation, collecting information, analyse, and formulate inferences and apply these in to the agri field. Such farmer is a scientist in reality., * Advantage of 'Sunday farming' or .Family farming' ?, Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, - utilization of barren land, - get pesticide free and fresh food, - exercise for the body, - recreation also, * Ways to overcome the lack of space for cultivation and limitation in nurturing ?, - Terrace cultivation, Grow bag cultivation, Vertical farming etc.
Page 9 :
[Class 8 - BS Unit 12 (Biology 4)], , 4. WHY CLASSIFICATION ?, , * Taxonomy : is the branch of biology that identifies organisms, classifies them on the basis of similarities and, differences and names them scientifically., The scientist, Carl Linnaeus, who fixed taxonomic hierarchy and provided a scientific base for classification,, is known as the 'Father of Modern Taxonomy'., * Taxonomic keys: are the scientific indicators used for identifying and classifying living beings. Of which, the, dichotomous keys are important and this keys has two possibilities of selection., [For instance, With incisors -without incisors, Claws that can be withdrawn -not withdrawn,, With wings – without wings, Having a pair of feet – not feet etc. are two different criteria for identification], Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty, 9846626323, , * Scientists who tried to classify organisms :, Aristotle, The Father of, BC. 384-322 (Greece), Biology, , Classified organisms as those with red blood cells, and those without red blood cells., , Theophrastus, BC. 371-287 (Greece), , The Father of, Botany, , Classified plants into, annuals, biennials and perennials., , Charakan, AD.1st century (India), , The Father of, Ayurveda, , He wrote the treatise 'Charaka Samhita' which included the, details of around 200 plants and animals, , John Ray, Used the term, Recorded more than 18000 plants in the book, AD. 1627-1705 (England) ‘species’ first time. ‘Historia Generalis Plantarum’, Carl Linnaeus, AD. 1707-1778 (Sweden), , The Father of, * Suggested the taxonomic hierarchy, as,, Modern Taxonomy Species – Genus – Family – Order / Series – Class –, Phylum – Kingdom., * Proposed binomial nomenclature, the scientific naming of, organisms using Genus name and Species name., , Robert H.Whittaker, AD. 1920-1980 (America), , Classified organisms in 5 kingdoms, as., Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia., , Carl Woese, AD. 1928-2012 (America), , Included organisms in 6 kingdoms under 3 Domains, (Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya), , * Method of classification by Carl Linnaeus (Examples in animals) :, Taxonomic, hierarchy, , Example-1, Cat, , Example-2, Dog, , Example-3, Man, , a. Kingdom, , Animalia (all animals), , Animalia, , Animalia, , b. Phylum, , Chordata (vertebrates/ with backbone), , Chordata, , Chordata, , c. Class, , Mammalia (with milk feeding glands), , Mammalia, , Mammalia, , d. Order, , Carnivora (having teeth to tear off flesh), , Carnivora, , Primates, , e. Family, , Felidae (having with-drawable claws), , Canidae, , Hominidae, , f. Genus, , Felis (small sized body, no roaring sound), , Canis, , Homo, , g. Species, , domesticus (features of the domestic cat), , familiaris, , sapiens
Page 11 :
Class 8 - BS Unit 13 (Biology 5), , 13. Diversity for Sustenance, * Ecology - The study of interaction among organisms and between the organisms and their surroundings., * Biosphere – Life existing region of earth, including soil, atmosphere and water., Abiotic factors, essential for the existence of biotic (living) factors, are sunlight, soil, air and water., Sun is the chief source of energy in the biosphere., Green plants convert light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis., * Producers – Green plants, that produce food by fixing energy through photosynthesis., * Consumers - Organisms that depend on plants directly or indirectly for food., The consumers that directly depend on plants are called primary consumers , those that feed on primary, consumers are called secondary consumers and those that feed on secondary consumers are called, tertiary consumers., * Food chain – A series of organisms that transfer energy through food., eg :- Grass - Grasshopper - Calotes - Eagle, Paddy – Hen - Eagle, Phytoplankton – Zooplankton - Fish -Seal - Shark, * Food web – A network of organisms that transfer energy through food among each other. (A net work of, food chains)., * Trophic level – The term which indicate the position of an organism in the food chain., First trophic level, Second trophic level, Third trophic level, Fourth trophic level, Producers, (plants), , Primary consumers, (herbivores), , Secondary consumers, (carnivores), , eg :- Paddy, Grass,, eg:- Hen, Grasshopper,, Plantain, Coconut palm, Deer, Man, , eg:- Man, Eagle, Snake,, Frog, , Tertiary consumers, (Those who feed on, carnivores too), eg:- Lion, Vulture, Eagle,, Crocodile, , * Ecological Interactions (food relations), 1. Predation, 2. Parasitism, , 3. Competition, , 4. Mutualism, , 5. Commensalism, , Beneficial to one,, Beneficial to one,, harmful to the other harmful to the other, (Prey becomes the, food of the predator), , Harmful to both., (Beneficial to the, one who wins the, competition), , Beneficial to both, , Beneficial to one,, Neither beneficial or, harmful to the other, , Eg:- Flower and, butterfly, , Eg:- Mango tree and, vanda (മരവാഴ), , Eg:- Deer and tiger,, Cat and rat., , Eg:- Mango tree and Eg:- Paddy and, loranthus(ഇതി, weeds, ളകണി), , * Kinds of ecosystems : Forest, Ocean, Grassland, Tundra, Wetland, Desert, Sacred groves(കാവ്), Marshy, land, Pond....., * Biodiversity :- All the diverse organisms that inhabit the earth along with their ecosystems., [It includes * ecosystem diversity, * species diversity * genetic diversity], (The term 'biodiversity, which means richness of the biosphere, is first used by a British environmentalist, Walter. G. Rosen, in1985), * Benefits of conserving biodiversity :* Availability of essential materials (Food, Medicine, Fuels, Construction materials...), * Cultural services (Aesthetics, Recreation, Study, Rituals and their practice ...), * Ecological Services (Soil formation, Prevention of soil erosion, O2-CO2 balance, Availability of, fresh water, Control of flood, Climate control ..), * Auxiliary services (Nutrient cycling, Pollination, Biological control, Seed dispersal ...)
Page 12 :
* Reasons for depletion of biodiversity ?, - Large scale destruction of ecosystems,, - Excessive use of chemicals in agricultural fields,, - Hunting,, - Over exploitation of the natural resources,, - Mining,, - Tourism, - Construction of dams obstructing the flow of rivers,, * A few extinct species due to depletion of biodiversity :- Dodo bird, Passenger pigeon, Quagga (കാടസീബ) ..., * A few endangered species due to depletion of biodiversity :- Saraca indica,Tree turmeric, Malabar civet cat,, Nilgiri Tahr, Lion-tailed macaque, Malabar hornbill ..., * Red Data Book:- A list of endangered plants and animals, prepared every year under the auspices of IUCN, (International Union for Conservation of Nature), an organization for environmental protection., * Methods of conservation of animals and plants :1. in-situ conservation method (organisms are protected in their natural habitats)., Eg:- Wild life sanctuary, National parks, Community reserves, Biosphere reserve, Sacred, groves (കാവകള) ..., 2. ex-situ conservation method (organisms are protected outside their natural habitats)., Eg:- Zoologicalgardens, Botanical gardens, Gene banks .., A. Wild life sanctuary, , B. National park, , C. Community reserve, , D. Biosphere reserve, , * Protection of, ecosystems, * Protection of wild, animals, mainly., , * Protection of, wild animals and plants., * Protection of historical, monuments, natural, resources and geographical features of an area., , * Conservation with, * Includes wild life sanctuapeople's participation., ries and National parks., * Ecologically, * Vast regions designed to, important places located protect world's important, in populated areas., ecosystems, biodiversity, and genetic resources., , eg:- Peppara, Periyar,, Wayanad, , eg:- Eravikulam, Silent, eg:- Kadalundi, eg:- Nilgiri,, Valley,Anamudi Shola,, Agasthyarkoodam, Mathikettan Shola,, Pambadum Shola, Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty, 9846626323, , * Sacred groves :- Small areas of biodiversity protected in regions inhabited by human beings., * Ecological hotspots :- Ecologically very important areas, rich in endemic species, but facing the threat of, habitat destruction., There are 34 hotspots all over the world,, Of which, Indian are - 1. Western Ghats, 2. North-Eastern Himalayas , 3. Indo-Burma region, A. Zoological gardens, B. Botanical gardens, C. Gene Banks, * Different varieties of animals are * Research centres where rare, * Research centres with facilities to, protected and housed separately, and important plants of diverse, collect seeds and gametes to, and where necessary arrangespecies are protected., preserve them for a long time, ments are made available for, their reproduction., eg:- Zoological gardens at, eg:- JNTBGRI at Palode in, eg:- RGCB Thiruvananthapuram, Thiruvananthapuram and Thrissur, Thiruvananthapuram and MBG, at Olavanna in Kozhikode, * Examples for International organisations design and coordinate environment protection activities. :, a. IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) ,, Headquarters - Switzerland., Aim – The protection of biodiversity., b. WWF (World Wide Fund for Nature) ,, Headquarters - Switzerland., Aim – Conservation of biodiversity, prevention of exploitation and pollution of, natural resources.
Page 13 :
14. For the Continuity of Generations, , Class 8 - BS Unit 14 (Biology 6), , 1.Two mode of reproduction ?, • Sexual reproduction (occur due to the union of male and female gametes), • Asexual reproduction (occur with out the union of gametes)., 2. Examples of asexual reproduction :, Binary fission in bacterium (under favourable conditions, bacterium cell divides in to two), Spore formation in fungus (under favourable conditions, spore develop in to new organism), Budding in hydra (bud, formed from parent body, grows and separates to develop new, organism), Carpel, 3.Sex organs in plants ?, Stamen, Flowers (Male organ is stamen and female organ is carpel), 4. Stages of sexual reproduction in plants :, - Pollination (falling of pollen grain on the stigma), - Formation and growth of pollen tube, (male gametes form from generative nucleus), - Fertilization (union of gametes) to form zygote., Stamen, , Carpel, , Anther, , Ovary, , Pollen grain, , Ovule, , Generative nucleus, , Female gamete/Egg, , Male gamete/Sperm, , Fertilization, Zygote, Embryo, 5. Formation of male gametes and fusion :, One Pollen grain, Tube nucleus, (disintegrates), , Generative nucleus, Male gamete, +, Egg, , Male gamete, +, Polar nuclei, , Zygote, , Endosperm, , Embryo, , Stored food for, embryo growth, , Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, , A pollen grain contains two nuclei such as, generative nucleus and tube nucleus., The generative nucleus divides to form, twomale gametes, while the tube nucleus, gets disintegrate., One male gamete fuses with the egg to form, zygote (ie, fertilization) while the other, male gamete fuses with the polar nuclei, seen in the ovary to form endosperm., , 6. Sex organs in human beings ?, Male organ is testis and female organ is ovary.
Page 14 :
7. Stages of sexual reproduction in human beings :, - Fertilization (union of gametes) to form zygote., - Growth of embryo in the uterus till parturition., Testis, , Ovary, , Male gamete/Sperm, , Female gamete/Ovum/Egg, , Fertilization, Zygote, , Embryo, Foetus, Baby, , 8., SPERM, , The male gamete, sperms ,are produced inside a, pair of testis. The female gamete, ovum is produced, inside any one of the ovaries and released to the, oviduct or the fallopian tube., Only one sperm fuses with the ovum to form, zygote (ie, fertilization) with in the oviduct. The, zygote undergoes division tobecome embryo,, which in turn attaches to the inner layer of uterus, (endometrium)., This area becomes the placenta, from which the, umbilical cord developes. A membraneous, covering, called amnion, developes around the, embryo and further growth of foetus complete with, in it., After 270-280 days of gestation, fully grown, baby comes out through the vagina (parturition)., OVUM, , - Male gamete - Motile - Microscopic, - Female gamete - Non motile - Larger, - Elongated with a head, middle piece and tail - Round with outer protective layers, Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323, , 9. The favourable body temperature for the formation of sperms in the testes ?, 35-360C, 10. ------ is the duct that carries sperms from the testes to the ureter., Vas deferens., 11. -------- is the duct that carries ovum to the uterus., Oviduct / Fallopian tube., 12. ------- secretes nutritional fluid for the male gametes., Prostate glands., 13. The male sex hormone produced by the testes ?, Testosterone., 14. The female sex hormones produced by the ovaries ?, Estrogen and Progesteron., 15. The process of secretion of sperms along with its nutritional fluid, is called ------- ., Insemination., 16. The process of releasing mature ovum from the ovary, is called ------ ., Ovulation., 17. The process through which the tissues expel out along with blood and mucus, through the, vagina, if fertilization fails to occur, is called ......... ., Menstruation., 18. The inner layer of the uterine wall ?, Endometrium.
Page 15 :
19. The role of placenta, umbilical cord and amnion in the growth and development of embryo ?, Placenta is the part by which the embryo attaches, itself to the endometrium. It supplies oxygen and, nutrients and also eliminates waste materials, through the umbilical cord., Amnion is the membraneous covering that, secretes amnion fluid to protect the foetus from, dehydration and external shock., 20. The gestation period of human beings is about ------ days., 270 – 280 days., 21. Different stages of growth in human beings ?, Infancy – Childhood – Adolescence – Adulthood – Old age., 22. The significance of adolescence ?, Adolescence is a period of rapid changes from childhood to adulthood. (11 to 19 years)., This is a period from the onset of puberty to the completion of physical growth., Development of brain, rapid increase in height and weight and increased efficiency of glands, are the significant features of this period., Along with the rapid physical changes, intense mental and emotional changes make, adolescence a significant period in one's life., 23. Physical changes in adolescence., In boys, In girls, - Fast growth., - Fast growth., - Growth of sex organs gains momentum. - Growth of sex organs gains momentum., - Hair grows in various parts of the body. - Hair grows in the pubic region and the, (pubic region, armpits, face, chest), pubic region and armpits., - Pitch of the voice deepens., - Pitch of the voice becomes sharp., - Glands in the skin become more active., - Glands in the skin become more active, breast, develops., - Shoulder bones expand., - Hip bones widen., - Ejaculation starts., - Menstruation starts ., 24. Why is adolescence said to be a period of challenges ?, Rapid changes in the development of the brain and in the production of hormones during, adolescence cause mental and emotional disturbances. A lack of awareness about one’s own, personality during this period leads to immature decision making., 25. Why is the rate of adolescence growth higher in girls than in boys?, Because the parts of brain that control physical and mental changes develop rapidly in girls., 26. The supply of iron folic acid tablets to students is meant for preventing ----------- ?, Anaemia., 27. What is anaemia ?, Anaemia is a condition caused by the reduction in the number of RBCs or deficiency of, haemoglobin. Anaemic person feels weak and exausted due to low oxygen transport in blood., 28. Suggest good food habits to growing adolescents., Do not skip breafast.Have right quantity of food at the right time.Choose a diet that includes, fruits, vegetables and pulses. Reduce the intake of fried food items. Use sugar and salt in, limited quantities. Do not be habituated to bottled drinks, packet food and fast foods., 29. Give examples for bad habits that affect our health., Smoking, consumption of alcoholic beaverages, abuse of drugs etc., 30. How is smoking injurious to health ?, Smoking and the use of tobacco products cause of cancer in the mouth, lungs, throat etc., Smoking reduces the diameter of blood capillaries and prevents the diffusion of oxygen., Rasheed Odakkal, GVHSS Kondotty 9846626323