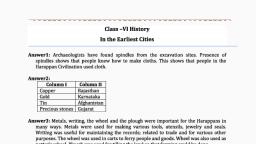
Page 1 :
Chapter – 04 Geography, Agriculture, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, •, , •, , •, •, , •, •, , •, , •, , Economic activities are of three types: (i) Primary Activities, (ii) Secondary Activities, (iii), Tertiary Activities., Primary activities are those activities which are connected with extraction and production of, natural resources, for example, agriculture, fishing, etc., Secondary activities are concerned with the processing of natural resources to, manufacturing products like baking of bread, weaving of cloth, etc., Tertiary activities provide services like transport, trade banking, insurance, advertising, etc., Agriculture is a primary activity which include growing crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and, rearing of livestock., 50% of persons in the world are engaged in agricultural activity., 2/3 of India’s population is still dependent on agriculture., Favourable topography of soil and climate are vital for agricultural activity. The land on, which the crops are grown is known as arable land., Farm System:, (i), Agriculture or farming is a system in which seeds, fertilizers, machinery and labour, are important inputs., (ii), Ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting are some of the operations., (iii) The outputs from the system include crops, dairy, wool and poultry products., Type of Farming:, (i), Farming depends upon the geographical conditions, demand of produce, labour and, level of technology., (ii), Subsistence farming and commercial farming are the two types of farming., Subsistence Farming: Subsistence farming is practices to meet the needs of the farmer’s, family., Intensive Subsistence Agriculture: In this farming, the farmer cultivates a small pot of land, using simple tools and more labour. Rice is the main crop. Other crops include wheat, maize,, pulses and oil seeds., Primitive Subsistence Agriculture: Primitive subsistence agriculture includes shifting, cultivation and nomadic herding., Shifiting Cultivation: In shifting cultivation, after cultivation the soil is abandoned and the, cultivator moves to a new plot. Shifting cultivation is also known as ‘slash and burn’, agriculture., Nomadic Herding: In nomadic herding, herdsmen move from place to place with their, animals for fodder and water along defined routes. Sheep, yak and goats are the herding, animals., Commercial Farming: In commercial farming crops are grown and animals are reared, grown and animals are reared for sale in market.
Page 2 :
•, , •, •, •, , •, •, •, , Commercial Grain Farming: In commercial grain farming crops like wheat and maize are, grown for commercial purpose. This farming practiced in temperate grasslands of North, America, Europe and Asia., Mixed Farming: In mixed farming, the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and, rearing livestock., Plantation: Plantations are a type of commercial farming where single crop of tea, coffee,, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton are grown., Major Crops: A variety of crops or many crops are grown to meet the requirement of the, growing population. Major crops of India are: Rice, Wheat, Millets, Maize, cotton, jute, coffee,, tea., Agriculture Development: Agricultrure Development refers to efforts made to increase, farm production in order to meet the growing demand of increasing population., A Farm in India: A typical Indian, Munna Lal has a farmland of about 1.5 hectares. He, purchases high yielding varieties of seeds from the market every alternate year., A Farm in the USA: The average size of a farm in the USA is about 250 hectares. The farmers, grow corn, soyabean, wheat, cotton and sugarbeet.