Page 1 :
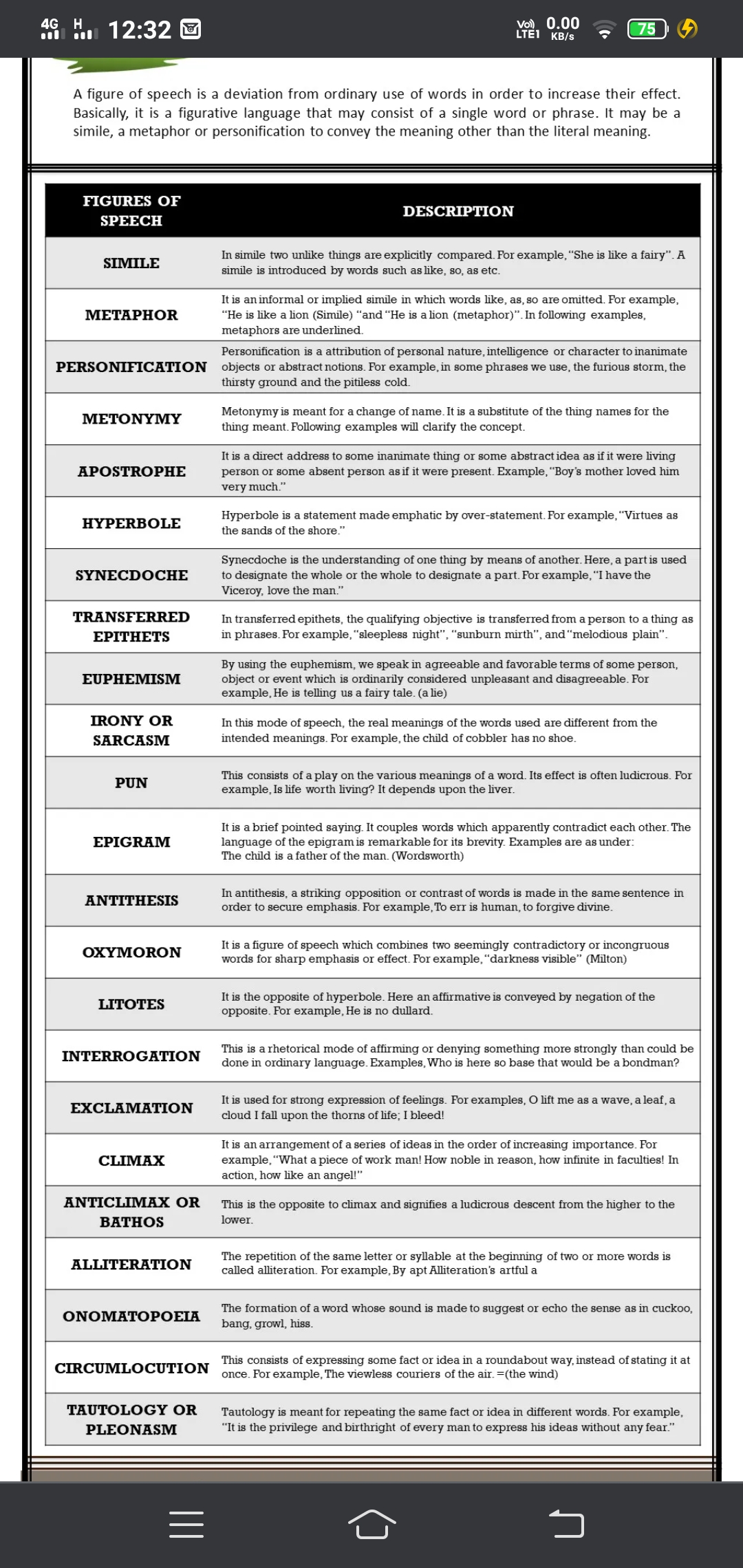
pT Pa 2, , No A), Pas aCe, , A figure of speech is a deviation from ordinary use of words in order to increase their effect., Basically, it is a figurative language that may consist of a single word or phrase. It may be a, simile, a metaphor or personification to convey the meaning other than the literal meaning., , FIGURES OF, SPEECH, , SIMILE, , DESCRIPTION, , Insimile two unlike things are explicitly compared. For example, “She is like a fairy”. A, simile is introduced by words such aslike, so, as etc., , , , METAPHOR, , Itis aninformal or implied simile in which words like, as, so are omitted. For example,, “He is like a lion (Simile) “and “He is alion (metaphor)". In following examples,, metaphors are underlined., , , , PERSONIFICATION, , Personification is a attribution of personal nature, intelligence or character to inanimate, objects or abstract notions. For example, in some phrases we use, the furious storm, the, thirsty ground and the pitiless cold., , , , METONYMY, , Metonymy is meant for a change of name. It is a substitute of the thing names for the, thing meant. Following examples will clarify the concept, , , , APOSTROPHE, , Itis a direct address to some inanimate thing or some abstract idea as if it were living, person or some absent person asif it were present. Example, “Boy's mother loved him, very much.”, , , , HYPERBOLE, , Hyperbole is a statement made emphatic by over-statement. For example, “Virtues as, the sands of the shore.”, , , , SYNECDOCHE, , Synecdoche is the understanding of one thing by means of another. Here, a partis used, to designate the whole or the whole to designate a part. For example, “I have the, Viceroy, love the man.”, , , , TRANSFERRED, EPITHETS, , In transferred epithets, the qualifying objective is transferred from a person to a thing as, in phrases. For example, “sleepless night”, “sunburn mirth”, and “melodious plain”, , , , EUPHEMISM, , By using the euphemism, we speak in agreeable and favorable terms of some person,, object or event which is ordinarily considered unpleasant and disagreeable. For, example, He is telling us a fairy tale. (a lie), , , , IRONY OR, SARCASM, , In this mode of speech, the real meanings of the words used are different from the, intended meanings. For example, the child of cobbler has no shoe., , , , PUN, , This consists of a play on the various meanings of a word. Its effect is often ludicrous. For, example, Is life worth living? It depends upon the liver, , , , Itis a brief pointed saying. It couples words which apparently contradict each other. The, language of the epigramis remarkable for its brevity. Examples are as under:, The child is a father of the man. (Wordsworth), , , , In antithesis, a striking opposition or contrast of words is made in the same sentence in, order to secure emphasis. For example, To err is human, to forgive divine., , , , Itis a figure of speech which combines two seemingly contradictory or incongruous, words for sharp emphasis or effect. For example, “darkness visible” (Milton), , , , LITOTES, , Itis the opposite of hyperbole. Here an affirmative is conveyed by negation of the, opposite. For example, He is no dullard., , , , INTERROGATION, , This is a rhetorical mode of affirming or denying something more strongly than could be, done in ordinary language. Examples, Who is here so base that would be a bondman?, , , , EXCLAMATION, , Itis used for strong expression of feelings. For examples, O lift me as a wave, aleaf,a, cloud I fall upon the thorns of life; I bleed!, , , , CLIMAX, , Itis an arrangement of a series of ideas in the order of increasing importance. For, example,”"What a piece of work man! How noble in reason, how infinite in faculties! In, action, how like an angel!”, , , , ANTICLIMAX OR, BATHOS, , This is the opposite to climax and signifies a ludicrous descent from the higher to the, lower., , , , ALLITERATION, , The repetition of the same letter or syllable at the beginning of two or more words is, called alliteration. For example, By apt Alliteration’s artful a, , , , ONOMATOPOEIA, , The formation of a word whose sound is made to suggest or echo the sense as in cuckoo,, bang, growl, hiss., , , , CIRCUMLOCUTION, , This consists of expressing some fact or idea in a roundabout way, instead of stating it at, once. For example, The viewless couriers of the air. =(the wind), , , , TAUTOLOGY OR, PLEONASM, , , , Tautology is meant for repeating the same fact or idea in different words. For example,, “Itis the privilege and birthright of every man to express his ideas without any fear.”