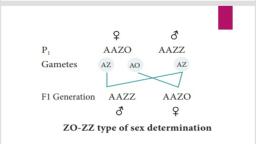
Page 1 :
Human, , , , Sex Dete ation, , , , > Sex determination mechanism in humans is XX=XY type., , > In humans 23 pairs of chromosomes are present. Of which 22 pairs are same in, both males and females. These are called autosomes., , > A pair of X chromosomes is present in the females whereas one X and one Y, chromosomes are present in males., , > During spermatogenesis in males, 50% sperms are produced with X chromosomes, and the remaining 50% sperms are produced with Y chromosomes beside the, autosomes., , > Females produce only one type of ovum with an X chromosome., , > There is an equal probability of fertilisation of the ovum by the sperm carrying, the X or Y chromosome., , > In case, the ovum is fertilised by a sperm carrying X chromosome, the zygote, develops into a female and the fertilisation of ovum with Y chromosome carrying, sperm results into a male offspring., , > Thus the genetic makeup of the sperm determines the sex of the child., , Genic Balance Theory, , > This is also called Ratio theory, proposed by Calvin Bridges to explain sex determination, in Drosophila melanogaster., , > The basic sex determination method in Drosophila is XX-XY type. Diploid male is 6XY, and diploid female is 6XX., , > Bridges crossed triploid female (9XXX) with normal male and observed different, karyotypes in the offspring., , > Bridges observed non-disjunction of allosome in both males and female flies during, gametogenesis., , > Non-disjunction is the failure of separation of paired chromosomes in anaphase | of, meiosis | ( Primary non-disjunction) or sister chromatids of a chromosome in anaphase II of, meiosis Il ( Secondary non disjunction), , >» Females produce AXX and AO gametes due to both primary and secondary nondisjunction., , > Males produce AXY sperms due to primary non-disjunction and AXX and AYY sperms due, to secondary non-disjunction., , > Bridges also studied the offspring resulting from the non-disjunction of X-chromosomes, during meiosis in females., > In the above crosses Bridges noticed offspring with different karyotypes , some of them, are aneuploids., > Aneuploidy is a state of chromosomal complement that is not a multiple set of the, haploid of chromosomes. ( 2n+1, 2n-1 etc) ., > From the results of the above crosses, Bridges concluded that, > 1) in Drosophila, genes for maleness are located on autosomes., > 2) gens for femaleness are located on X chromosomes, > 3) Y chromosome lacks male determining factors, but contains genetic information, essential for male fertility, > 4) the factor determining the sex is the ratio of X chromosomes to the number of, haploid sets of autosomes, > Sex index= Number of X chromosomes(X) / Number of autosomal sets (A)