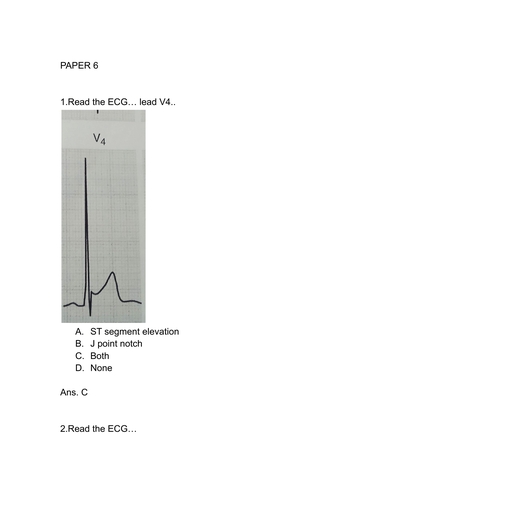
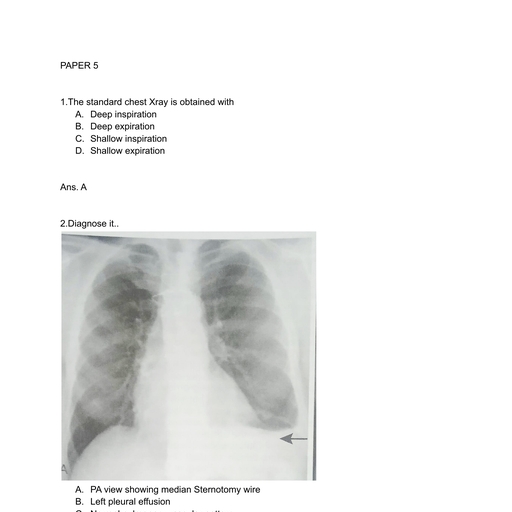
Page 1 :
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE…. NOTES SERIES… PART 1.., CHAPTER 1...INTRODUCTION, Marfan's syndrome which is the results of mutation in the gene that encodes, fibrillin-1., The right and left ventricle do not function in series in fetus as they do in extra uterine, circulation., About 60% of the umbilical venous return that is oxygenated in the placenta bypasses, the liver through the ductus venosus and enters IVC and right atrium., The Electrocardiogram developed in 1903 by William Einthoven., The x-ray was developed in 1895 by ROENTGEN., CHAPTER 2…..NORMAL OR INNOCENT MURMURS, Murmurs that occur in the absence of either morphologic or physiologic, abnormalities of heart or circulation are called innocent murmurs., , All normal systolic murmur are midsystolic except mammary souffle., PULMONARY ARTERY SYSTOLIC MURMUR, Midsystolic…, Maximal intensity in second left intercostal space., Commonly heard in pregnant women with anemia., BRANCH PULMONARY ARTERY SYSTOLIC MURMUR, Found in neonates., SUPRACLAVICULAR SYSTOLIC MURMUR, Maximal above clavicle., SYSTOLIC MAMMARY SOUFFLE, Systolic murmur, The murmur is heard over breast late in pregnancy., AORTIC SYSTOLIC MURMUR IN OLDER ADULTS, Aortic sclerosis systolic murmur of older age., GALLAVARDIN DISSOCIATION, Musical high frequency murmur within left ventricular cavity and the harsh impure, right basal murmur within aortic root., NORMAL BICUSPID AORTIC VALVE, Midsystolic murmur that is most prominent in the second right intercostal space in, children., CARDIORESPIRATORY MURMUR, Benign nature., VENOUS HUM, Normal continuous murmur., Maximal intensity in SUPRACLAVICULAR fossa.
Page 5 :
LEFT ISOMERISM, , Visceral Heterotaxy with left ISOMERISM tend to occur in females and right, ISOMERISM in Males., , CHAPTER.. 4...ISOLATED CONGENITAL COMPLETE HEART BLOCK, Complete heart block… atrial impulses are not conducted to ventricles., An association between Maternal lupus erythematous and congenital complete heart, block was reported in 1966., CHB is passively transferred autoimmune disease that affects offspring of mother, with Ro/SSA auto antibodies., Dilation of the ascending aorta is present in large proportion of pediatric patients with, isolated congenital heart block., A pulse rate slow for age leads to diagnosis of congenital CHB., The upstroke is brisk and pulse pressure relatively wide., Cannon waves are found in CHB., , CANNON WAVES IN CONGENITAL CHB.
Page 6 :
Fourth heart sound are found. They are not heard in healthy young people., The P wave of atrial activity and the QRS of ventricular activity occur independently., , ECG SHOWING CHB., , CHAPTER 5...CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES OF PERICARDIUM, , The pericardium consists of two layers. The layer attached to the surface of heart is, the visceral pericardium., The layer that is not attached to the surface of heart is parietal pericardium. It is, separated from the visceral pericardium by 20 to 50 ml of serous ultrafiltrate of, plasma., CANTRELL'S SYNDROME.., Ectopia cordis, Epigastric omphalocele, Cleft of distal sternum, Defects of anterior diaphragm, Defect of diaphragmatic pericardium, , HISTORY, In partial or complete absence of pericardium, the most common symptoms is chest, pain that appears suddenly in previously asymptomatic adults., The pain is stabbing, left sided, brief, unrelated to exertion but aggravated by position, especially left lateral decubitus, awakens patients from sleep and is relieved in, upright position., The pain associated with partial absence of left pericardium is attributed to herniation, of left atrial appendage through pericardial defect., The pain associated with complete absence of pericardium is believed to originates, from torsion of thoracic inlet., Additional symptoms include Dyspnea, Palpitations, Dizziness, syncope and most, commonly sudden death.
Page 7 :
PHYSICAL APPEARANCE, Abnormal facies, GH deficiency, VATER defects, ARTERIAL PULSE AND JVP, Normal., , CONGENITAL PARTIAL ABSENCE OF PERICARDIUM, With congenital partial absence of left pericardium, the position and movement of the, heart are normal., With complete absence, a striking mobility of heart shifts to the left., , A. .. Xray from 10 year old girl shows a relatively long left paracardiac convexity, caused by congenital Intra pericardial aneurysm of left atrial appendage.., B. Schematic illustration of the congenital Intra pericardial aneurysm of left atrial, appendage, , X-RAY, Congenital partial absence of the left pericardium is accompanied by herniation of the, left atrial appendage, represented in the x-ray by convexity immediately below, pulmonary trunk or if herniation is larger by extension of convexity to the second and, third left interspace., A congenital pericardial cyst typically present as a smooth homogeneous radio, density in the right cardiophrenic angle, touching anterior chest wall and anterior, portion of right hemidiaphragm.
Page 8 :
X-RAY from a 23 year old women with an usually large congenital pericardial cyst, (arrow) that occupies entire right cardiac border., A congenital complete absence of pericardium is characterised by dramatic mobility, of heart that results in striking leftward and posterior displacement., ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, The echocardiogram may strongly suggest the diagnosis of congenital absence of, pericardium and can be used to identify Coexistent cardiac defects., SYMPTOMS, LEFT sided chest pain, Dyspnea, Palpitation, Dizziness, Syncope, Sudden death, , DEFINITIVE DIAGNOSIS, Thoracic MRI, CT SCAN, , CHAPTER 6….CONGENITALLY CORRECTED TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT, ARTERIES, Karl Von Rokitansky applied the term corrected to a undescribed form of, transposition of great arteries., The aorta is positioned left and anterior., The right sided ventricle is finely trabeculated as usually seen in left sided ventricle., The left Atrioventricular valve and left sided ventricle resembled the usual right, Atrioventricular valve and right ventricle., From the right sided ventricle arises somewhat right and posteriorly positioned, pulmonary artery., The atria are normal.
Page 9 :
Transposition of the great arteries are characterised.. by chambers that are joined, Concordant at the Atrioventricular junction but discordantly at the ventriculo great, arterial junction., The pulmonary artery arises from a morphologic left ventricle and the aorta arises, from morphologic right ventricle., The circulation are in parallel rather than in series., Congenitally Corrected Transposition of the great arteries is characterised by, chambers that are joined discordantly at the Atrioventricular junction and ventricles, that are joined discordantly at the ventriculo Great arterial junction., Atrioventricular alignment and Ventriculoarterial alignment are both Discordant., The double Discordance physiologically corrects the Discordance intrinsic to each, other., , Also called as L-transposition., , TO.. BE CONTINUED…….