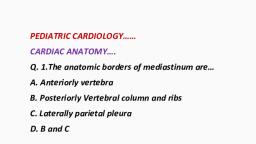
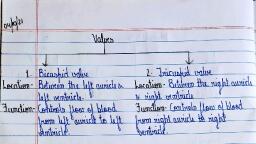
Page 1 :
PARTIALLY ANOMALOUS PULMONARY VENOUS CONNECTION…. Part 1, In partially anomalous pulmonary venous connection, the left sided pulmonary veins, usually connect anomalously to derivatives of the left cardinal system(CS and left, innominate vein)., Anomalous connection of the right pulmonary vein usually are to derivatives of the, right cardinal system(SVC or inferior vena cava)., The most common type of PAPVC is of the left pulmonary veins to the left internal, jugular vein., The second most common types are anomalous connection of pulmonary vein from, the right lung to inferior vena cava., , Above diagram shows partially anomalous pulmonary venous connection…, The right pulmonary vein may drain into right superior vena cava or into the right, atrium without being abnormally connected to them., The upper lobe drain by one large or two or three smaller veins into superior vena, cava below azygos vein, SCIMITAR SYNDROME.., All the right pulmonary vein or occasionally the veins draining the right middle and, right lower lobes enter the IVC either just above or below the diaphragm., This malformations, termed the Scimitar syndrome., Frequently is associated with other anomalies including hypoplasia of right lung,, anomalous arterial connection to the right lung from aorta and pulmonary, sequestration., , Scimitar syndrome…, Left innominate vein is the usual site of anomalous connection of the left pulmonary, vein., The connecting vein between the left pulmonary veins and LIV also has been called a, persistent left superior vena cava.
Page 2 :
Above diagram shows catheter angiogram showing PAPVC of the LPVs to the inferior, vena cava.., LSVC.., The LSVC which is located immediately behind the left atrial appendage., An LSVC connect either with the CS or with the LA when the CS is unroofed., When an left pulmonary vein drains into LSVC, the LSVC also should connect with the, CS or with the LA., PHYSIOLOGY, The fundamental physiologic disturbance of PAPVC is similar to that of ASD, that is, increased pulmonary blood flow, as a consequence of recirculation of oxygenated, blood through the lungs., The factors that determine the hemodynamic state include the number of, anomalously connected veins, the cross sectional area of the anomalously draining, pulmonary vascular bed, the site of the anomalous connection, the presence or, absence of ASD and size of ASD., , To be continued……..