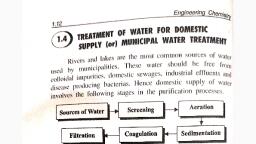
Page 1 :
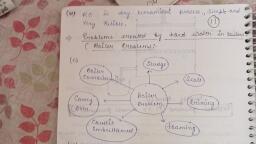
its Treatment, , neni Sg, 1.6 BOILER TROUBLES (OR) BOILER FEED WATER, , The water fed into the boiler for the productic, called boiler feed water. Boiler feed water should be free, ea turbidity, oil, dissolved gases, alkali and hardness snatig, , ‘anes: 1 hard water obtained from natural sources is fed, the boilers, the following troubles may arise., , NM Of steam, , — substances, directly into, , Boiler troubles (or) disadvantages of using hardwater in hoilers, , 1. Formation of Scales and sludges in boilers,, 2. Priming and foaming (carry over)., , 3. Caustic embrittlement., , 4. Boiler corrosion., , 1.6.1 Formation of Scales and Sludges in boilers, , ‘When water is continuously converted into steam in, boilers (or) heat exchangers, the concentration of dissolved salts, _ in water increases progressively. When the concentration of the, salts reaches their saturation point, they are thrown out in the, , Hard adhering, Loose precipitate See Le, eepeeated th, Sone . boiler (scale), (sludge) Boiler., , , , (b), ) Scale in boiler, , (a), Vig. 1.4 (a) Sludge in boiler (b.
Page 2 :
,, , Engineering Chemigy, , 1 20 _emioseenientner, et —, form 0 we ipi § ol iC inne, { reel] itales on t!, , i “asl solu ile O, , s, The le, exchangers. The, , 1. Sludge (Loose deposit), , If the precipitate is loose, , SIudges are formed, MgSO, and CaCl. They, , than cold water., , 2, Seale (Hard deposit), On the other hand, if the, , adherent coating on the inner wall, , r wa ae, re gels precipitated first,, , py the subst, have greater solubilities in hot water, , tis of the boilers (or) he, , and slimy it is called sludge, ances. like MgCh, Mgco,,, , precipitate forms hard and, s of the boiler, it is called, , scale. Scales are formed by substances like Ca(HCO3),,, , CaSO, and Mg(OH)o., , Table 1.1 Comparison of Scales and Sludges, , , , , , Sludge is a loose, slimy, and non-adherent, precipitate., , , , Scale is a hard, adherent, coating. |, , , , , , 2. |The main sludge forming, substances are MgCOs,, , MgCl,, MgSO,, CaCl etc,., , and, , , , , , , The main scale forming, substances are Ca(HCO3)),, , CaSO,, Mg(OH))., , , , 3 Disadvantages: Sludges, are poor conductors of, heat. Excess of sludge, formation decreases the, efficiency of boiler,, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Disadvantages: Scales act, as thermal insulators. It, decreases the efficiency of, boiler. Any crack, developed on the - scale,, leads to €xplosion
Page 3 :
its Treatment, : ae 1.21, , prevention Prevention, , Sludge formation can] (i) — Scale formation ¢, be prevented by be. prevented “an, using softened water. dissolving using faa, like HCl, H,SO,., , (i), , , , (ii) Sludges can also be|(ii) Scale formation can, removed by be removed by, “blow-down (a) External, operation”. treatment., , (b) Internal, , treatment., , , , , , (iii) Blow-down operation They can also be, is a process of removed by applying, removing a portion thermal shocks,, of concentrated water scrapers, wire brush,, by fresh water etc.,, frequently from the, boiler during steam, production., , , , , , , , , , | Disadvantages of Scale Formation, , 1. Wastage of fuels, Scales have low thermal conductivity,, from boiler to inside water is not efficient., on supply of heat to water, overheating i, re wastage of fuel. The wastage of fuel depends, ness and nature of the scale, which, , so the heat transfer, , In order to provide, s done and this, on the, , is shown in the table., , , , 0.325, 10%, , , , Thickness of scale (mm), [Wastage of fuel
Page 4 :
rF rt~—‘—, , a, , Engineering Chemistry, , , , 2. Decrease in efficiency, , ¢ -ondensers, alves and conder, , ‘ sposit. in the valve i ai ,, Seales sometimes deposit m ase efficiency of, , Thi s in decre, of the boiler and choke. ‘This result, , the boiler,, , 3. Boiler explosion sae eben cote, , Sometimes due to over heating the t ° i niterke, crack and causes sudden contact of high heated boi OF sewn, with water. This causes formation of a large amount 0 on, and high pressure is developed which may lead to explosion., , Prevention of scale formation, , 1 At the initial stage, scales can be removed using, scraper, wire brush etc., , ty, , If scales are brittle, they can be removed by, thermal shocks., , %3) By using suitable chemicals like dil. acids (for, CaCO3 scale), EDTA (for CaSO, scale) with, , which they form suitable complexes., , 4 If the scales are loosely adhering, they can be, removed by frequent blow down Operation., , 1.6.2 Priming and Foaming (carry over), , During the production of steam in, boiling, some droplets of liquid water, steam. Steam containing droplets of liq, steam. These droplets of liquid water carry with them some, dissolved salts and suspended impurities. This Phenomenon is, called carry over. It occurs due to priming and foaming., , the boiler, due to rapid, are carried along with, uid water is called wet, , 1. Priming, , Priming is the process of production, , of wet steam., Priming is caused by, , (i) High steam velocity., (ii) Very high water level in the boiler,
Page 5 :
and Its Tf nndanienin, , (iii) Sudden boiling of water,, , (iv) Very poor boiler design,, prevention, priming can be controlled by, , i) Controlling the velocity of steam., \ YAS, , (, (ii) Keeping the water level lower!, , (iil) Good boiler design., , (iv) Using treated water., , 9, Foaming, The formation of stable bubbles above the surface of, water is called foaming. These bubbles are carried over by, , steam leading to excessive priming., Foaming is caused by the, , (i) presence of oil, and grease,, (ii) presence of finely divided particles., , Prevention, Foaming can be prevented by, , (i) adding coagulants like sodium aluminate,, , aluminium hydroxide,, (ii) adding anti-foaming —_ agents like, polyamides., , synthetic, , 1.6.3 Caustic Embrittlement (Intercrystalline, Cracking), , _ Caustic embrittlement means inte, boiler metal., , rcrystalline cracking of, , Boiler water usually contains 2 small proportion ot, this Na ,CO3 undergoes, , NayC03, In high pressure boilers, , decomposition to give NaOH. (Huda mt