Page 1 :
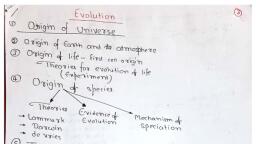
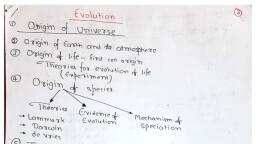
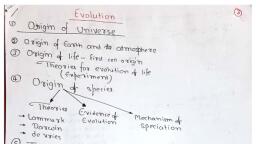
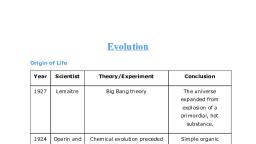
we °e, , Evolution, , , , , , NCERT Crisp, , ey, , Sullar distances are measured in light years., The universe is very old ~ almost 20 billion years old., , ‘The Big Bang theory attempts to explain to us the Origin of, universe., , ‘The Big Bang theory: It states that the universe was in a, very high density state and then expanded., , + Asingular huge explosion unimaginable in physical term, The universe expanded and hence the temperature came, down. Hydrogen and helium formed sometime later, , The gases condensed under gravitation and formed the, galaxies of the present day universe., , In the solar system of the Milky Way galaxy, earth was, supposed to have been formed about 4.5 billion years, back., , Conditions of early earth, * Earth formed 4.5 billion years back., * There was no atmosphere on early earth., , * Water vapor, methane, carbon dioxide and ammonia, released from molten mass covered the surface, , * The UV rays from the sun broke up water into hydrogen, and oxygen and lighter H, escaped., , Oxygen combined with ammonia and methane to form, Water, CO, and others., , The ozone layer was formed., , AS it cooled, the water vapor fell as rain, to fill all the, depressions and form oceans., , scmmation of, Life appeared 500 million years after the f, earth,, , Origin of life, , Early Greek thinkers thought units of life, called spores were transferred to different planets, including earth., , Theory of Panspermia (Cosmozoic theory), This theory was proposed by Richter(1865), , According to this theory life on earth came from a distant, planet in the form of spores or microorganisms,, , Theory of Spontaneous Generation, , According to this theory, life came out of decaying and rotting, matter like straw, mud, etc., , Theory of spontaneous generation was proposed by Van, Helmont., , Theory of Biogenesis: According to this theory, life originated, from pre-existing life., , This theory was proved by three scientists: Redi, Spallanzani, and Pasteur., , Louis Pasteur Experiment, , Careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only, from pre-existing life., , He showed that in pre-sterilized flasks, life did not come from, killed yeast while in another flask open to air, new living, organism arose from ‘killed yeast’., , This disproved the theory of spontaneous generation., , emus esa, , Oparin — Haldane theory of origin of life ‘, Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the, first form of life could have come from pre- existing nonliving organic molecule (e.g. RNA, protein etc.)., Formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution,, ic. formation of diverse organic molecule from inorganic, constituents.
Page 2 :
_~, Urey and Miller experiment, © Fie Conditions on earth were 4, *« High temperature., ©... + Volcanic storms., « Reducing atmosphere containing CH,, NH,, water and, y * _ bydrogen, etc., In 1953, S.L. Miller, an ‘American Scientist, created similar, conditions in a laboratory scale., He created electric discharge in a closed flask to raise, temperature upto 800°C as it was in primitive earth., , Used CH, H,, NH, and water vapor inside the flask., , Acceptance of chemical evolution theory: (evidences), , + Miller observed the synthesis of amino acids from, simple inorganic chemicals in simulated condition in the, laboratory., , + In similar experiments others observed formation of, sugars, nitrogen bases, pigment and fats., , « Analysis of meteorite content also revealed similar, compounds indicating that similar processes are occurring, elsewhere in space., , , , , , The first non-cellular forms of life could have originated, 3 billion years back. ., * They would have been giant molecules (RNA, proteins,, polysaccharides, etc)., , + These capsules reproduced their molecules perhaps,, \ named as coacervates,, , © The first cellular forms of life were probably unicellular., | © All life forms were in water environment only., , + This theory of biogenesis from non-liv ing molecules was, _ accepted by majority., , ife Forms — A Theory, , , , ATOLL, , , , * Conventional religious literature tells us about the theory, of special creation,, The theory of special creation has three connotations:~, , * All the living organisi i : doce cctah Pia ae (species types) that we see today, , The diversity was al . ‘ :, Siteacle Rice. ways the same since creation and will, , * Earth is about 4000 years old., , Challenge to special creation theory by Darwin, , + Charles Darwi, ee concluded that existing life forms share, es LO varying degrees not only among themselves, , Homologous organs | O, ‘ bat, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , put also with life forms that’existed millions of yeary 4, , + Many such life forms do not exist any more, The, q, been extinctions of different life forms in the y Te hag, by just as new forms of life arose at different peri,0™, , history of earth. ds of, , There has been gradual evolution of life forms,, , Any population has built in variation in characteristics, , Those characteristics which enable some to survive, , in natural conditions (climate, food, physical factors, <3, , would outbred others that arc less-endowed to tava,, , under such natural condition. e, , + Survival of the fittest: The fitness, according to 7, refers ultimately and only to reproductive fitness; leave,, more progeny than others., , + These, therefore, will survive more and hence are selecieg, by nature. He called it as natural selection., , + Alfred Wallace, 4 naturalist who worked in Malay, , Archipelago had also come to similar conclusions around, , the same time., , The geological history of earth closely correlates with the, , biological history of earth., , , , , , What Are The Evidences For PA ed, , Evolution is @ stochastic process based on chance events in, nature and chance mutation in the organisms., , A. Paleontological evidence:, The study showed that life-forms varied” over time and, certain life forms are restricted to certain geological, timespans. Hence, new lives have arisen at different times, in the history of earth., , + Fossils: Remains of hard parts of life-forms found in, rocks. A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers, indicates the gcological period in which they existed., , + Rocks: Rocks form sediments and a cross-section of, earth's crust indicates the arrangement of sediments one, over the other during the long history of earth., , 8. Comparative anatomy and morphological evidence:, , + Comparative anatomy and morphology shows similarities, and differences among organisms of today and those, existed years ago,, , Homologous and analogous organs, , , , , , Have fundamental simi »| Have similar function, in structure and origin | different structure, but different functions. It} origin, , indicates common ancestry., , , , and
Page 3 :
_| of vertebrates sad hungs, Convergent and divergent evolution, an Divergent evolution, , , , le is the process by which, | unrelated species become, more similar in order to, sarvive and adapt in similar, | eavironmental condition, , , , , , It is the process by which, related species become less, similar in order to survive, and adapt in different, environmental condition, , , , 1, , origin of homologous, , , , , , , , The orig Origin of analogous organ:, omgans is due to divergent|is due to convergent, evolution. | evolution., , Embryological support for evolution, , C, l‘ Proposed by Ernst Haeckel based upon observation of, certain features during embryonic stage common to, all vertebrates that are absent in adult., , The embryos of all vertebrates including human develop, a row of vestigial gill slits just behind the head but it is a, functional organ only in fish and not found in any other, adult vertebrates., , This is disproved on careful study performed by Karl, Ernst von Baer. He noted that embryos never pass, through the adult stages of other animals., , D. Evolution by natural selection, , Based on observation of moth population in England made, im 1850., Industrial melanism (In England), , Before industriatization (1850s), , There were more white winged, on trees than dark winged of, , D ered the trees., ‘ ichen cov fe, Reason: There was white sr moths survived but, , In that und, the white wi, , Goeuh cadens moths were picked out by predators., After industrialization (192), , More dark winged moths and less, , Reason: The tree —, , smoke and soot. No growth o!, the white winged moth did not surv”, identified them easily. Dark winged, , , , , , , moths (Bistor bemlaria), melanised moths (Biston, , white winged moths., dark due to industrial, i Under this condition, , renee the predators, , moth survived because, , , , Ye, , ep) * Excess use of herbicides,, 1), ), , Tesulted in selection of resistant vari, , Maseuin ieties in a much lesser, , This is also true for microbes against which we employ, , antibiotics or drugs against cukaryotic organisms/cell,, Hence, resistance Organisms/cells are appearing in a time, scale of months or years and not in centuries., , * The process of evolution of different species in a given, geographical area starting from a point and literally, radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is, called adaptive radiation., , + When more than one adaptive radiation appeared to have, occurred in an isolated geographical area (representing, different habitats), one can call this convergent evolution., , Examples:, © Darwin's Finches, * In Galapagos Islands, Darwin observed small black, birds later called Darwin's Finches., , + He realized that there were many varieties of finches in, the same island,, , * All the varieties, evolved on the island itself., , + From the original seed-cating features, many other, , forms with altered beaks arose, enabling them to become, insectivorous and vegetarian finches., , © Australian marsupial, = A number of marsupials cach different from the other, evolved from an ancestral stock. But all within the, Australian istand continent,, © Placental mammals, , * In Australia, placental mammals also exhibit adaptive, radiation in evolving into varieties of such placental, mammals each of which appears to be ‘similar’ to a, corresponding marsupial (e.g., placental wolf and, Tasmanian wolf-marsupial)., , Darwinian theory of evolution, , + Branching descent and natural selection are the two, key concepts of Darwinian Theory of Evolution., , + The rate of appearance of new forms is linked to the life, cycle or the life span., , + Some organisms are better adapted to survive in an, otherwise hostile environment., , + Adaptive ability is inherited. It has genetic basis, for, getting selected and to evalve., , + Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and get, selected by nature.
Page 4 :
j, , Lamarck theory of evolution: (Theory of inheritance of, acquired characters), , + It states that evolution of life forms occurred by use and, disuse of organs., , Evolution by use of organs, * Long neck of giraffe is due to continuous elongation to, forage leaves on tall trees. This acquired character was, inherited to succeeding generations., Evolution by disuse of organs, * Disappearance of limbs in snakes., = This theory was eliminated out because it is proved that, the characters are inherited only through genes., , Mechanism of Evolution, , Hugo de Vries proposed Mutation Theory of evolution., He conducted some experiments on Ocnothera lamarckiana, (evening primrose) and believed that evolution takes place, through mutation and not by minor variation., , Differences between Darwinian variation & devries, mutation, , , , , , , , , , , , , , Darwinian Evolution DeVries Mutation |, Minor variation Large variation, Slow and directional Random, sudden and direction, less, Gradual evolution Speciation by saltation {single, step, large mutation), , , , , , , , In a given population one can find out Hardy-Weinberg, principle stated the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a, gene on a locus using algebraic equations., , ‘The principle states that allele frequencies in a population are, , Operation of natural selection on different traits, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and is constant from generation to generation,, , stable, enes and their alleles in a Population,, , ene | (total gem, en a Smiths This is called genetic eq, , Sum total of all the allelic frequencies is 1., , (p+ay= pt 2pat a= ©, , When frequency measured, differs from expected values,, ome (direction) indicates the extent of evola, change. Y, Disturbance in genctic equilibrium, or Hardy-Wein, principle Le., change of frequency of alleles in a populatiog, would then be interpreted as resulting In evolution., , Five factors are known (0 affect Hardy-Weinberg equilip., , rium:, , « Gene migration or gene flow., , + Genetic drift., , + Mutation., , + Genetic recombination., , + Natural selection., Gene migration, When migrations of 8 section of population to another place, occur, gene frequencies change in the original as well as in, the new population, New genes falleles are added to the new, population and these are lost from the old population,, , en ae UU, , Gene flow, Gene migration occurs many time is termed as gene flow., , Genetic drift, , Change in gene frequency takes place by chance. Genetic drift, is seen only in small population., , Genetic drift also called Sewall wright effect or scattering of, variablity., , Founder effect, , Sometimes the change in allelic frequency is so different in, the new sample of population that they became @ i, species. The original drifted population becomes, species and the effect is called founder effect., , , , , , PE: ‘Directional selection, , , , Disruptive selection, , , , , , In this,, mean character value, , uals acquire, , More individuals acquire value other, than the mean character value., , More individuals acquire peripheral, character value at both ends of the, distribution curve, , , , , , | Peak gets higher and narrower, , Peak shifts in one direction, , Two peaks form, , , , , , E.g., plant height, human birth weight, , E.g., DDT resistance in mosquitoes, , , , Sickle cell anaemia, , , , Medium sized individuals, are favoured, , Number of individesls, , , , , , ‘Numaber of individuals, , , , (A=, , ‘Two peaks form, , Wal