Page 1 :
DRUGS ACTING ON AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM (ANS), General consideration of ANS: Human nervous system broadly divided into:, , Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): The peripheral nervous system consists of the Somatic nervous system (SNS) and, Autonomic nervous system (ANS). The somatic nervous system consists of sensory neurons, and motor neurons. The sensory neurons carry the messages from the peripheral to the CNS., The ANS consists of general visceral sensory (afferent) neurons and supplies, innervation to smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands and visceral organs., The word Autonomic is derived from two words:, Auto – Self and Nomos – Regulating, It means that the Autonomic nervous system is self-regulating involuntary system, because it regulates the physiological reactions or the action of ANS is not under will power., For example, Function of heart, pupillary size regulation in particular light response., Autonomic functions include control of respiration, cardiac regulation (the cardiac, control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex actions such as, coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting.
Page 2 :
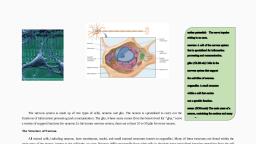
The activity of nervous system is performed by the nerve cells called Neurons. Neuron, is the fundamental unit of nervous system., Functions of Neurons: 1. Generation of impulse., 2. Conduction of impulse., 3. Transmission of impulse., ANS consist of both the branches:, 1. Myelinated preganglionic fiber, 2. Non-myelinated postganglionic fiber
Page 3 :
The autonomic motor pathways consist of sets of two motor neurons and autonomic, ganglion. A ganglion is usually a group of nerve cell bodies lying outside the CNS or the, synapse between post-ganglionic fiber and pre-ganglionic fiber is known as Ganglion while, the synapse between post-ganglionic fiber and effector or receptor is known as neuro effector, junction., An autonomic ganglion is a cluster or group of nerve cell bodies (a ganglion) i.e.,, sympathetic and parasympathetic in the autonomic nervous system. In autonomic motor, pathway, the first neuron has its cell body in CNS and its axon extends from the CNS to, autonomic ganglion. The second motor neuron has its cell body in autonomic ganglion and its, axon extends from the autonomic ganglion to effector organ., The first motor neuron which is present before the ganglion (Cell body in the brain or, spinal cord) is called as Preganglionic neuron and the myelinated axon is termed as, Preganglionic fiber. The second motor neuron which is present after the ganglion (cell body, in ganglion) and extended to the effector organ is called as Postganglionic neuron and its axon, (Non-myelinated) termed as Postganglionic fiber.
Page 4 :
The ANS comprises of two major divisions: Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions., The preganglionic neurons of sympathetic nervous system originated from the Thoracic, and Lumber vertebrae (T1 to L2) of the spinal cord (Thoraco-Lumber outflow). Whereas the, preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system originated from the cranial, nerves (III, VII, IX & X) and the sacrum (S2, S3 & S4) portion of the spinal cord (Cranio-Sacral, outflow)., The parasympathetic preganglionic neurons are long, while the postganglionic neurons, are short. Whereas the sympathetic preganglionic neurons are short and the postganglionic, neurons are large., , Presynaptic membrane, synaptic cleft and postsynaptic membrane together called as Synapse., The space between the neuron and muscle or effector cell is known as Synaptic cleft. The, vesicles which store the synthesized neurotransmitter like adrenaline or acetylcholine are, known as Synaptic vesicles. The electrical potential difference across the cell membrane is, called Action potential.
Page 5 :
The depolarization, also called the rising phase, is caused when positively charged sodium ions, (Na+ & Ca++) suddenly enters through open voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels into a, neuron. The excitatory effect is due to depolaeization., , Repolarization phase also called falling phase, it occurs just after the depolarization. This is, due to efflux of K+ ions through voltage gated potassium channels., , FIGHT TO FLIGHT / EMERGENCY, , REST AND DIGEST SYSTEM
Page 6 :
SYMPATHOMIMETIC AGENTS/ ADRENAERGIC AGENT/, ADRENOMIMETIC AGENTS, These are the agents which produces similar response to that of stimulation of, sympathetic nervous system, called Sympathomimetic agents., Stimulation of SNS, releases neurotransmitter Adrenaline. That means,, Sympathomimetics are the agents which produces similar response to that of adrenaline, hence, sympathomimetics are also called as Adrenergic Agents., Stimulation of sympathetic nervous system releases three endogenous bioamines like, Adrenaline (Epinephrine), Nor-adrenaline (Nor-epinephrine) and Dopamine. These three, bioamines are also called as Catecholamines because they possessed catechol basic nucleus in, their structure., Location of release of catecholamines: 1. Adrenaline (Adr): - Adr a major hormone released by adrenal medulla directly into, the blood later it distributes through blood and reaches to its site of action and acts on, its alpha and beta receptor produces physiological response., 2. Nor-Adrenaline (NA): - It released at postganglionic sympathetic sites except sweat, glands and vasodilator fiber., 3. Dopamine (DA): - A major neurotransmitter in Basal ganglia, CTZ, Anterior pituitary, etc. and limited at periphery i. e. Renal blood vessels etc., Receptor and its location: The adrenergic receptors are of two types i. e. Alpha (α) Receptor and Beta (β), Receptor., Receptor, , α1, , α2, , Blood vessels of, Skin and mucosa, Constriction, , Location/, Organ, , Eye, Mydriasis, (Dilation of pupil), Uterus, Contraction, GIT, Constipation, , Pancreas, Beta cells, Decreases, insulin, secretion, , β1, , β2, , Heart, Increases Heart rate,, cardiac output and, blood pressure, , Coronary Blood, Vessels, Vasodilation, , Fat cells, Lipolysis, , Bronchial, Smooth muscles, Bronchodilation, , Kidney, Increases Renin, secretion, Posterior Pituitary, Releases, Antidiuretic, hormone, , Liver, Gluconeogenesis, Fat cells, Lipolysis, , β3, Fat cells, Lipolysis, , Detrusor, (Urinary, Bladder Muscle), Relaxation
Page 7 :
Synthesis, Storage and Release of Catecholamines: -, , The noradrenergic neurons also called adrenergic neurons, synthesizes, store and, release noradrenaline as their neurotransmitter. Catecholamines are synthesized from the, amino acid phenylalanine a dietary material which is then absorbed from intestine and in liver, the phenylalanine converted into Tyrosine by the enzyme hepatic phenylalanine hydroxylase., Then this Tyrosine circulates into the blood stream and transported into the noradrenergic, neurons. Within the neuron, tyrosine converted into DOPA by tyrosine hydroxylase and DOPA, to Dopamine (DA) by dopa-decarboxylase. Then Dopamine enters into the storage vesicle and, here it is converted into Nor-adrenaline by enzyme Dopamine beta hydroxylase. The formed, noradrenaline is then stored into the Synaptic vesicles., On the other hand in Adrenal medulla, noradrenaline further converted into Adrenaline, by enzyme N-methyltransferase. The conversion of noradreanline to adrenaline does not occurs, in adrenergic neurones, but this conversion takes place in adrenal medulla., The synthesized noradreanline is stored in synaptic vesicles, when impulse reached, towards nerve terminal, the synaptic vesicles get ruptured and by the process of exocytosis, releases neurotransmitter Noradrenaline into the synaptic cleft. After releasing some amount, of noradrenaline forms a complex with its adrenoreceptor shows biological response, some of, the noradrenaline is re-uptake into the neuron for further synthesis and some amount of, noradrenaline is then metabolized by an enzyme Catechol-O-methyltransferase and, Monoamino Oxidase.
Page 8 :
On the other hand the adrenaline is released from adrenal medulla and then this, adrenaline directly forms a complex with its adrenoreceptor and shows biological response., The adreanline also metabolizes by an enzyme Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and, Monoamino Oxidase (MAO)., Metabolism and Excretion of Adrenaline and Nor-adrenaline: -, , Metanephrine, , •, , Nor-Metanephrine, , The metabolites are then excreted through kidney in the form of urine., , CLASSIFICATION OF SYMPATHOMIMETIC AGENTS: A. According to its activity / Mechanism of Action: 1. Directly Acting Sympathomimetics: These drugs directly act on Alpha or Beta or on both Alpha and Beta receptors., i. Alpha receptor Agonist: Eg.,, , Nor-Adrenaline,, , Phenylephrine,, , Oxymetazoline,, , Xylometazoline,, , Clonidine, Apraclonidine., ii. Beta receptor Agonist: Eg., Isoprenaline, Dobutamine, Salbutamol, Terbutaline, Salmeterol., iii. Alpha and Beta Receptor Agonist: Eg., Adrenaline.